Abstract
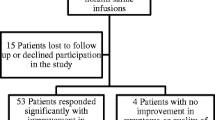
Orthostatic intolerance (OI) is common in teenagers (T) and young adults (A). Despite treatment with oral fluids, medication, and exercise, a significant number have symptoms from multiple organ systems and suffer low quality of life (QOL). Previous studies showed that acute intravenous (IV) hydration (IH) could help restore orthostatic tolerance; however, no data are available about the intermediate-term effects of IH. We therefore studied the efficacy of IH to improve QOL and manage medication-refractory OI patients. Our study population consisted of 39 patients (mean age = 16.1 ± 3.3) years; thirty-two were female. Average number of medications failed = 3.1. Average QOL score on self-reported OI questionnaire was 4.2 (normal QOL = 10). IV hydration consisted of normal saline (1–2 l/day, 3–7 days/week). 1) Orthostatic testing revealed Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia (24), Neurally Mediated Hypotension (14) or OI (1). 2) Average orthostatic change in heart rate was 48 ± 18 bpm. 3) IH was performed via intermittent IV access (10), PICC line (22), and Port (7). 4) Duration of IH varied from 1 week to 3.8 years (mean = 29 ± 47 weeks). 5) Overall, 79 % (n = 31) demonstrated clinically improved self-reported QOL. 6) Six patients who discontinued IH requested to restart treatment. (7) Complications consisted of upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (n = 3) and infection (n = 4). IH is an effective therapy to improve QOL in T&A with medication-resistant OI. Most patients continued to report improved QOL once IH was discontinued. IH should be considered a therapeutic option in medication-resistant OI patients with low QOL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antiel RM, Risma JM, Grothe RM et al (2008) Orthostatic intolerance and gastrointestinal motility in adolescents with nausea and abdominal pain. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 46(3):285–288
Bellard E, Fortrat JO, Custaud MA, Victor J, Greenleaf J, Lefthériotis G (2007) Increased hydration alone does not improve orthostatic tolerance in patients with neurocardiogenic syncope. Clin Auton Res 17(2):99–105
Benarroch EE (2012) Postural tachycardia syndrome: a heterogeneous and multifactorial disorder. Mayo Clin Proc 87(12):1214–1225
Bogert LW, Wesseling KH, Schraa O et al (2010) Pulse contour cardiac output derived from non-invasive arterial pressure in cardiovascular disease. Anaesthesia 65(11):1119–1125
Burklow TR, Moak JP, Bailey JJ et al (1999) Neurally mediated cardiac syncope: autonomic modulation after normal saline infusion. J Am Coll Cardiol 33(7):2059–2066
Carew S, Connor MO, Cooke J et al (2009) A review of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Europace 11(1):18–25
Charkoudian N, Halliwill JR, Morgan BJ, Eisenach JH, Joyner MJ (2003) Influences of hydration on post-exercise cardiovascular control in humans. J Physiol 552(Pt 2):635–644
Chelimsky G, Chelimsky TC (2013) Gastrointestinal manifestations of pediatric autonomic disorders. Semin Pediatr Neurol 20(1):27–30
Delarbre B, Dabadie A, Stremler-Lebel N et al (2014) Introduction of the use of a pediatric PICC line in a French University Hospital: review of the first 91 procedures. Diagn Interv Imaging 95(3):277–281
Diab Y, Sharma K Incidence of thrombosis following PICC insertion. Pers Commun
Faulkner MS, Hathaway D, Tolley B (2003) Cardiovascular autonomic function in healthy adolescents. Heart Lung 32(1):10–22
Figueroa RA, Arnold AC, Nwazue VC et al (2014) Acute volume loading and exercise capacity in postural tachycardia syndrome. J Appl Physiol 117(6):663–668
Finlay JB, Hartman AF, Weir RC (1995) Post-swim orthostatic intolerance in a marathon swimmer. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27(9):1231–1237
Fu Q, Vangundy TB, Galbreath MM et al (2010) Cardiac origins of the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(25):2858–2868
Haruna Y, Takenaka K, Suzuki Y, Kawakubo K, Gunji A (2014) Effect of acute saline infusion on the cardiovascular deconditioning after 20-days head-down tilt bedrest. J Gravit Physiol 5(1):P45–P46
Jarjour IT (2013) Postural tachycardia syndrome in children and adolescents. Semin Pediatr Neurol 20(1):18–26
Kanin M, Young G (2013) Incidence of thrombosis in children with tunneled central venous access devices versus peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs). Thromb Res 132(5):527–530
Kizilbash SJ, Ahrens SP, Bruce BK et al (2014) Adolescent fatigue, POTS, and recovery: a guide for clinicians. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care 44(5):108–133
Kumar S, Babbar R, Varshney VP et al (2012) A study of autonomic nervous system status in children of asthmatic parents. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 56(1):74–79
Levin AB (1966) A simple test of cardiac function based upon the heart rate changes induced by the Valsalva maneuver. Am J Cardiol 18(1):90–99
Mehlsen J, Boesen F (1987) Substantial effect of acute hydration on blood pressure in patients with autonomic failure. Clin Physiol 7(3):243–246
Ojha A, Chelimsky TC, Chelimsky G (2011) Comorbidities in pediatric patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Pediatr 158(1):20–23
Piha SJ (1995) Autonomic responses to the Valsalva manoeuvre in healthy subjects. Clin Physiol 15(4):339–347
Rajashekar RK, Niveditha Y, Ghosh S (2003) Blood pressure response to cold pressor test in siblings of hypertensives. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 47(4):453–458
Sandroni P, Opfer-Gehrking TL, McPhee BR et al (1999) Postural tachycardia syndrome: clinical features and follow-up study. Mayo Clin Proc 74(11):1106–1110
Schofield J, Blitshteyn S, Shoenfeld Y, Hughes G (2014) Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and other autonomic disorders in antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome (APS). Lupus 23(7):697–702
Sullivan SD, Hanauer J, Rowe PC et al (2005) Gastrointestinal symptoms associated with orthostatic intolerance. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 40(4):425–428
Stewart JM (2013) Common syndromes of orthostatic intolerance. Pediatrics 131(5):968–980
Younoszai AK, Franklin WH, Chan DP, Cassidy SC, Allen HD (1998) Oral fluid therapy. A promising treatment for vasodepressor syncope. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 152(2):165–168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to this study to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moak, J.P., Leong, D., Fabian, R. et al. Intravenous Hydration for Management of Medication-Resistant Orthostatic Intolerance in the Adolescent and Young Adult. Pediatr Cardiol 37, 278–282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1274-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-015-1274-6