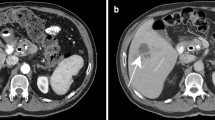
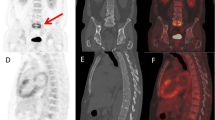
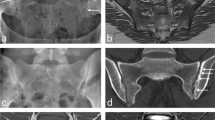
Abstract
The diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in adults is predominantly made by a combination of typical clinical features of flank pain, high temperature and dysuria combined with urinalysis findings of bacteruria and pyuria. Imaging is generally reserved for patients who have atypical presenting features or in those who fail to respond to conventional therapy. In addition, early imaging may be useful in diabetics or immunocompromised patients. In such patients, imaging may not only aid in making the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis, but more importantly, it may help identify complications such as abscess formation. In this pictorial review, we discuss the role of modern imaging in acute pyelonephritis and its complications. We discuss the growing role of cross-sectional imaging with computed tomography (CT) and novel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques that may be used to demonstrate both typical as well as unusual manifestations of acute pyelonephritis and its complications. In addition, conditions such as emphysematous and fungal pyelonephritis are discussed.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donnenberg M, Welch R (1996) Virulence determinants in uropathogenic E. coli. In: Mobley H, Warren J (eds) Urinary tract infection: molecular pathogenesis and clinical management. American Society for Microbiology Washington, DC, 135–174
Kawashima A, Sandler CM, Goldman SM, Raval BK, Fishman EK (1997) CT of renal inflammatory disease. Radiographics 17:851–868
Kawashima A, Sandler CM, Goldman SM (1998) Current roles and controversies in the imaging evaluation of acute renal infection. World J Urol 16:9–17
Johnson GL, Fishman EK (1997) Using CT to evaluate the acute abdomen: spectrum of urinary pathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168:273–276
Stamm WE, Hooton TM (1993) Management of urinary tract infections in adults. N Engl J Med 329:1328–1334
Scholes D, Hooton TM, Roberts PL, Gupta K, Stapleton AE, Stamm WE (2005) Risk factors associated with acute pyelonephritis in healthy women. Ann Int Med 142 (1):20–27 Jan 4
Sheffield JS, Cunningham FG (2005) Urinary tract infection in women. Obstet Gynecol 106 (5 Pt 1):1085–1092 Nov
Tseng CC, Wu JJ, Wang MC, Hor LI, Ko YH, Huang JJ (2005) Host and bacterial virulence factors predisposing to emphysematous pyelonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 46 (3):432–439
Kawashima A, Sandler CM, Ernst RD et al (1997) Renal inflammatory disease: the current role of CT. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 38:369–415
Goldman SM, Fishman EK (1991) Upper urinary tract infection: the current role of CT, ultrasound and MRI. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 12:335–360
Urban BA, Fishman EK (2000) Tailored Helical CT Evaluation of the Acute Abdomen. Radiographics 20:725–749
Zeman RK, Fox SH, Silverman PM et al (1993) Helical (spiral) CT of the abdomen. AJR Am J Roentgenol 160:719–725
Heiken JP, Brink JA, Vannier MW (1993) Spiral (helical) CT. Radiology 189:647–656
Wyatt SH, Urban BA, Fishman EK (1995) Spiral CT of the kidneys: role in characterization of renal disease I Nonneoplastic disease. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 36:1–37
Gold RP, McClennan BL, Rottenberg RR (1983) CT appearance of acute inflammatory disease of the renal interstitium. AJR Am J Roentgenol 141:343–349
Hoddick W, Jeffrey RB, Goldberg HI et al (1983) CT and sonography of severe renal and perirenal infections. AJR Am J Roentgenol 140:517–520
Ishikawa I, Saito Y, Onouchi Z et al (1985) Delayed contrast enhancement in acute focal bacterial nephritis: CT features. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:894–897
Cronan JJ, Amis ES, Dorfman GS (1984) Percutaneous drainage of renal abscesses. AJR 142 (2):351–354
Deyoe LA, Cronan JJ, Lambiase RE, Dorfman GS (1990) Percutaneous drainage of renal and perirenal abscesses: results in 30 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 155 (1):81–83 July
Kawashima A, Vrtiska TJ, LeRoy AJ, Hartman RP, McCollough CH, King BF (2004) CT Urography. Radiographics 24:S35–S54
Majd M, Nussbaum Blask AR, Markle BM, Shalaby-Rana E, Pohl HG, Park JS, Chandra R, Rais-Bahrami K, Pandya N, Patel KM, Rushton HG (2001) Acute pyelonephritis: comparison of diagnosis with 99 m-Tc DMSA, SPECT, spiral CT, MR imaging and power Doppler US in and experimental pig model. Radiology 218 (1):101–108
Kraus SJ (2001) Genitourinary imaging in children. Pediatr Clin North Am 48:1381–1424
Lonergan GJ, Pennington DJ, Morrison JC, Haws RM, Grimley MS, Kao TC (1998) Childhood pyelonephritis: comparison of gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging and renal cortical scintigraphy for diagnosis. Radiology 207:377–384
Poustchi-Amin M, Leonidas JC, Palestro C, Hassankhani A, Gauthier B, Trachtman H (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging in acute pyelonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 12:579–580
Geoghegan T, Govender P, Torreggiani WC (2005) MR urography depiction of fluid-debris levels: a sign of pyonephrosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 185:560
Kim B, Lim HK, Choi MH, Woo JY, Ryu J, Kim S, Peck KR (2001) Detection of parenchymal abnormalities in acute pyelonephritis by pulse inversion harmonic imaging with or without microbubble ultrasonographic contrast agent: correlation with computed tomography. J Ultrasound Med 20:5–14
Kim JH, Eun HW, Lee HK, Park SJ, Shin JH, Hwang JH, Goo DE, Choi DL (2003) Renal perfusion abnormality. Coded harmonic angio US with contrast agent. Acta Radiol 44 (2):166–171
Kawashima A, Sandler CM, Goldman SM (2000) Imaging in acute renal infection. Br J Urol Int 86 (Supp 1):70–79
Baumgarten DA, Baumgartner BR (1997) Imaging and radiologic management of upper urinary tract infection. Urol Clin North Am 24:545–569
Webb JA (1997) The role of imaging in adult acute urinary tract infection. Eur Radiol 7:837–843
Schainuck L, Fouty R, Cutler RE (1968) Emphysematous pyelonephritis. A new case and review of previous observations. Am J Med 44:134–139
Evanoff GV, Thompson CS, Foley R, Weinman EJ (1987) Spectrum of gas within the kidney: emphysematous pyelonephritis and emphysematous pyelitis. Am J Med 83:149–154
Kaplan DM, Rosenfield AT, Smith RC (1997) Advances in the imaging of renal infection. Helical CT and modern coordinated imaging. Infect Dis Clin North Am 11:681–705
Grayson DE, Abbott RM, Levy AD, Sherman PM (2002) Emphysematous infections of the abdomen and pelvis: A Pictorial Review. Radiographics 22:543–561
Grozel F, Berthezene Y, Guerin C et al (1997) Bilateral emphysematous pyelonephritis resolving to medical therapy: demonstration by US and CT. Eur Radiol 7:844–846
Patterson JE, Andriole VT (1997) Bacterial urinary tract infections in diabetes. Infect Dis Clinic North Am 11:735–750
Chen MT, Huang CN, Chou YH et al (1997) Percutaneous drainage in the treatment of emphysematous pyelonephritis: 10-year experience. J Urol 157:1569–1573
Joseph RC, Amendola MA, Artze ME et al (1996) Genitourinary tract gas: imaging evaluation. Radiographics 16:295–308
Langston CS, Pfister RC (1970) Renal emphysema. AJR Am J Roentgenol 110:778–786
Wan YL, Lee TY, Bullard MJ et al (1996) Acute gas-producing bacterial renal infection: correlation between imaging findings and clinical outcome. Radiology 198:433–438
Michaeli J, Mogle P, Perlberg S et al (1984) Emphysematous Pyelonephritis. J Urol 131:203–208
Papanicolaou N, Pfister RC (1996) Acute renal infections. Radiol Clin North Am 34:965–95
Stapleton A (2002) Urinary tract infections in patients with diabetes. Am J Med 8 (113 Suppl 1A):80S–84S
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stunell, H., Buckley, O., Feeney, J. et al. Imaging of acute pyelonephritis in the adult. Eur Radiol 17, 1820–1828 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0366-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0366-3