Abstract
Purpose
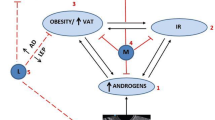
Glucagon-like peptides receptor agonists are currently approved as anti-obesity agents, yet the experience with their use in polycystic ovarian syndromes (PCOS)-related obesity and insulin resistance is still limited.
Methods
We examined the effects of liraglutide on obesity, insulin resistance, and androgen levels in PCOS through a meta-analysis.
Results
Seven RCTs where women with PCOS were treated with liraglutide were identified. The variables that were examined before and after a 90-day treatment included waist circumference, body mass index (BMI), fasting insulin concentrations, insulin resistance using homeostatic model (HOMA-IR), serum testosterone, and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). The analysis included 178 women. Only 172 patients had post-treatment measurements. While BMI significantly dropped by −1.65 (0.72–2.58) Kg/m2 after 3 months treatment with liraglutide, waist circumference did not change significantly. Similarly, fasting insulin levels, insulin sensitivity, and SHBG did not change significantly. However, serum testosterone decreased by 0.29 nmol/L in 88 women (P = 0.0003).
Conclusion
In a limited number of the women with PCOS, BMI and serum testosterone are only variables that significantly decrease after 3 months of treatment with GLP-1 receptor agonists. Larger sample size studies with longer durations of treatment may be required to examine potential benefits of these medications in improving insulin sensitivity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sirmans SM, Pate KA (2013) Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Epidemiol 6:1–13. doi:10.2147/CLEP.S37559
Azziz R, Woods KS, Reyna R, Key TJ, Knochenhauer ES, Yildiz BO (2004) The prevalence and features of the polycystic ovary syndrome in an unselected population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(6):2745–2749. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-032046
Balen AH, Conway GS, Kaltsas G, Techatrasak K, Manning PJ, West C, Jacobs HS (1995) Polycystic ovary syndrome: the spectrum of the disorder in 1741 patients. Hum Reprod 10(8):2107–2111
Glueck CJ, Dharashivkar S, Wang P, Zhu B, Gartside PS, Tracy T, Sieve L (2005) Obesity and extreme obesity, manifest by ages 20–24 years, continuing through 32–41 years in women, should alert physicians to the diagnostic likelihood of polycystic ovary syndrome as a reversible underlying endocrinopathy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 122(2):206–212. doi:10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.03.010
Legro RS, Castracane VD, Kauffman RP (2004) Detecting insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome: purposes and pitfalls. Obstet Gynecol Surv 59(2):141–154. doi:10.1097/01.OGX.0000109523.25076.E2
Niafar M, Nader ND (2015) Adiponectin as serum biomarker of insulin resistance in patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol Off J Int Soc Gynecol Endocrinol. doi:10.3109/09513590.2015.1008445
Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Dunaif A (2012) Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome revisited: an update on mechanisms and implications. Endocr Rev 33(6):981–1030. doi:10.1210/er.2011-1034
da Silva AM, de Andrade AC, Dias BH, da Silva Medeiros MA, Rao VS, das Chagas Medeiros F (2014) Elevated diastolic blood pressure in insulin-resistant polycystic ovarian syndrome patients. Arch Gynecol Obstet 289(1):119–122. doi:10.1007/s00404-013-2953-2
Holst JJ (1994) Glucagonlike peptide 1: a newly discovered gastrointestinal hormone. Gastroenterology 107(6):1848–1855
Kreymann B, Williams G, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (1987) Glucagon-like peptide-1 7–36: a physiological incretin in man. Lancet 2(8571):1300–1304
Mari A, Degn K, Brock B, Rungby J, Ferrannini E, Schmitz O (2007) Effects of the long-acting human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide on beta-cell function in normal living conditions. Diabetes Care 30(8):2032–2033. doi:10.2337/dc07-0310
Garber A, Henry R, Ratner R, Garcia-Hernandez PA, Rodriguez-Pattzi H, Olvera-Alvarez I, Hale PM, Zdravkovic M, Bode B, Group L-S (2009) Liraglutide versus glimepiride monotherapy for type 2 diabetes (LEAD-3 Mono): a randomised, 52-week, phase III, double-blind, parallel-treatment trial. Lancet 373(9662):473–481. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61246-5
Derosa G, Maffioli P (2012) GLP-1 agonists exenatide and liraglutide: a review about their safety and efficacy. Curr Clin Pharmacol 7(3):214–228
Monami M, Dicembrini I, Marchionni N, Rotella CM, Mannucci E (2012) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight: a meta-analysis. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:672658. doi:10.1155/2012/672658
Monami M, Dicembrini I, Nardini C, Fiordelli I, Mannucci E (2014) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(1):38–47. doi:10.1111/dom.12175
Vilsboll T, Christensen M, Junker AE, Knop FK, Gluud LL (2012) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on weight loss: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 344:d7771. doi:10.1136/bmj.d7771
Du Q, Wang YJ, Yang S, Zhao YY, Han P (2014) Liraglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Adv Ther 31(11):1182–1195. doi:10.1007/s12325-014-0164-2
Kahal H, Aburima A, Ungvari T, Rigby AS, Coady AM, Vince RV, Ajjan RA, Kilpatrick ES, Naseem KM, Atkin SL (2015) The effects of treatment with liraglutide on atherothrombotic risk in obese young women with polycystic ovary syndrome and controls. BMC Endocr Disord 15:14. doi:10.1186/s12902-015-0005-6
Elkind-Hirsch K, Marrioneaux O, Bhushan M, Vernor D, Bhushan R (2008) Comparison of single and combined treatment with exenatide and metformin on menstrual cyclicity in overweight women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(7):2670–2678. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-0115
Rasmussen CB, Lindenberg S (2014) The effect of liraglutide on weight loss in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: an observational study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 5:140. doi:10.3389/fendo.2014.00140
Jensterle M, Kocjan T, Kravos NA, Pfeifer M, Janez A (2015) Short-term intervention with liraglutide improved eating behavior in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocr Res 40(3):133–138. doi:10.3109/07435800.2014.966385
Jensterle M, Kravos NA, Pfeifer M, Kocjan T, Janez A (2015) A 12-week treatment with the long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist liraglutide leads to significant weight loss in a subset of obese women with newly diagnosed polycystic ovary syndrome. Hormones (Athens) 14(1):81–90
Jensterle Sever M, Kocjan T, Pfeifer M, Kravos NA, Janez A (2014) Short-term combined treatment with liraglutide and metformin leads to significant weight loss in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and previous poor response to metformin. Eur J Endocrinol 170(3):451–459. doi:10.1530/EJE-13-0797
Jensterle M, Kocjan T, Kravos NA, Pfeifer M, Janez A (2014) Short-term intervention with liraglutide improved eating behavior in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocr Res. doi:10.3109/07435800.2014.966385
Kahal H, Aburima A, Ungvari T, Rigby AS, Coady AM, Vince RV, Ajjan RA, Kilpatrick ES, Naseem KM, Atkin SL (2015) The effects of treatment with liraglutide on atherothrombotic risk in obese young women with polycystic ovary syndrome and controls. BMC Endocrine Disord 15(1):14. doi:10.1186/s12902-015-0005-6
Astrup A, Rossner S, Van Gaal L, Rissanen A, Niskanen L, Hakim A, Madsen J, Rasmussen MF, Lean ME, Group NNS (2009) Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 374(9701):1606–1616. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61375-1
Rosenstock J, Klaff LJ, Schwartz S, Northrup J, Holcombe JH, Wilhelm K, Trautmann M (2010) Effects of exenatide and lifestyle modification on body weight and glucose tolerance in obese subjects with and without pre-diabetes. Diabetes Care 33(6):1173–1175. doi:10.2337/dc09-1203
Clark AM, Thornley B, Tomlinson L, Galletley C, Norman RJ (1998) Weight loss in obese infertile women results in improvement in reproductive outcome for all forms of fertility treatment. Hum Reprod 13(6):1502–1505
Huber-Buchholz MM, Carey DG, Norman RJ (1999) Restoration of reproductive potential by lifestyle modification in obese polycystic ovary syndrome: role of insulin sensitivity and luteinizing hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(4):1470–1474. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.4.5596
Kahal H, Abouda G, Rigby AS, Coady AM, Kilpatrick ES, Atkin SL (2014) Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue, liraglutide, improves liver fibrosis markers in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Endocrinol 81(4):523–528. doi:10.1111/cen.12369
Diamanti-Kandarakis E (2006) Insulin resistance in PCOS. Endocrine 30(1):13–17. doi:10.1385/ENDO:30:1:13
Dunaif A (1997) Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome: mechanism and implications for pathogenesis. Endocr Rev 18(6):774–800. doi:10.1210/edrv.18.6.0318
Gambineri A, Pelusi C, Vicennati V, Pagotto U, Pasquali R (2002) Obesity and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Obesity Relat Metab Disord J Int Assoc Study Obesity 26(7):883–896. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0801994
Rincon J, Holmang A, Wahlstrom EO, Lonnroth P, Bjorntorp P, Zierath JR, Wallberg-Henriksson H (1996) Mechanisms behind insulin resistance in rat skeletal muscle after oophorectomy and additional testosterone treatment. Diabetes 45(5):615–621
Reaven GM (1995) Pathophysiology of insulin resistance in human disease. Physiol Rev 75(3):473–486
Pitteloud N, Hardin M, Dwyer AA, Valassi E, Yialamas M, Elahi D, Hayes FJ (2005) Increasing insulin resistance is associated with a decrease in Leydig cell testosterone secretion in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(5):2636–2641. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-2190
Nestler JE (1997) Insulin regulation of human ovarian androgens. Hum Reprod 12(Suppl 1):53–62
Poretsky L, Bhargava G, Saketos M, Dunaif A (1990) Regulation of human ovarian insulin receptors in vivo. Metab Clin Exp 39(2):161–166
Pasquali R, Casimirri F, De Iasio R, Mesini P, Boschi S, Chierici R, Flamia R, Biscotti M, Vicennati V (1995) Insulin regulates testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin concentrations in adult normal weight and obese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80(2):654–658. doi:10.1210/jcem.80.2.7852532
Yang M, Liu R, Li S, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Liu D, Wang Y, Xiong Z, Boden G, Chen S, Li L, Yang G (2013) Zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein is associated with insulin resistance in humans and is regulated by hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, or liraglutide administration: cross-sectional and interventional studies in normal subjects, insulin-resistant subjects, and subjects with newly diagnosed diabetes. Diabetes Care 36(5):1074–1082. doi:10.2337/dc12-0940
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niafar, M., Pourafkari, L., Porhomayon, J. et al. A systematic review of GLP-1 agonists on the metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovaries. Arch Gynecol Obstet 293, 509–515 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3976-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3976-7