Abstract
Purpose of Review
We review recent studies discussing the impact of pharmacologic agents for weight loss on clinical cardiovascular events, as well as cardiometabolic risk factors.
Recent Findings
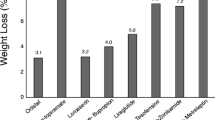
Pharmacotherapy with current FDA-approved medications for weight loss can significantly improve known risk factors for the development of cardiovascular disease such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, insulin resistance, inflammatory biomarkers, and the quantity of visceral fat, as well as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. However, data regarding the actual reduction in clinical cardiovascular events with the use of weight loss medications is scarce.
Summary
Pharmacotherapy for weight loss may have additional benefit in optimizing patient’s cardiometabolic comorbidities and improving their clinical cardiovascular outcomes, but each drug should be carefully selected based upon individual patient characteristics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. JAMA. 2010;303(3):235–41.
Pollack AA. AMA recognizes obesity as a disease. New York Times. Archived from the original on June. 2013;18.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Cancers associated with overweight and obesity make up 40 percent of cancers diagnosed in the United States [Press release]. Retrieved from: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2017/p1003-vs-cancer-obesity.html. (2017).
•• Heymsfield SB, Wadden TA. Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and management of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(3):254–66. Excellent recent review article on mechanisms, adverse effects and multimodal management of obesity.
•• Apovian CM, Aronne LJ, Bessesen DH, McDonnell ME, Murad MH, Pagotto U, et al. Pharmacological management of obesity: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(2):342–62. Endocrine Society Guidelines for pharmacotherapy in obesity.
Hampp C, Kang EM, Borders-Hemphill V. Use of prescription antiobesity drugs in the United States. Pharmacother J Hum Pharmacol Drug Ther. 2013 Dec 1;33(12):1299–307.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report: estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States, 2014. Atlanta: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2014.
Samaranayake NR, Ong KL, Leung RY, Cheung BM. Management of obesity in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 2007–2008. Ann Epidemiol. 2012;22(5):349–53.
Thomas CE, Mauer EA, Shukla AP, Rathi S, Aronne LJ. Low adoption of weight loss medications: a comparison of prescribing patterns of antiobesity pharmacotherapies and SGLT2s. Obesity. 2016;24(9):1955–61.
Ikeda N, Sapienza D, Guerrero R, Aekplakorn W, Naghavi M, Mokdad AH, et al. Control of hypertension with medication: a comparative analysis of national surveys in 20 countries. Bull World Health Organ. 2014;92(1):10–9C.
Colquitt JL, Pickett K, Loveman E, Frampton GK. Surgery for weight loss in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(8):CD003641.
Adams TD, Gress RE, Smith SC, Halverson RC, Simper SC, Rosamond WD, et al. Long-term mortality after gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(8):753–61.
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, Wolski K, Brethauer SA, Navaneethan SD, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes—3-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(21):2002–13.
Look AHEAD Research Group. Cardiovascular effects of intensive lifestyle intervention in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2013;2013(369):145–54.
•• Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, Greenway F, Halpern A, Krempf M, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):11–22. Landmark trial that demonstrated significant benefit weight loss with liraglutide.
•• Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;2016(375):311–22. Landmark trial demonstrating significant reduction in major cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with liraglutide.
Marso SP, Poulter NR, Nissen SE, Nauck MA, Zinman B, Daniels GH, et al. Design of the liraglutide effect and action in diabetes: evaluation of cardiovascular outcome results (LEADER) trial. Am Heart J. 2013;166(5):823–30.
Garvey WT, Ryan DH, Look M, Gadde KM, Allison DB, Peterson CA, et al. Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(2):297–308.
Fidler MC, Sanchez M, Raether B, Weissman NJ, Smith SR, Shanahan WR, et al. A one-year randomized trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in obese and overweight adults: the BLOSSOM trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(10):3067–77.
O’Neil PM, Smith SR, Weissman NJ, Fidler MC, Sanchez M, Zhang J, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in type 2 diabetes mellitus: the BLOOM-DM study. Obesity. 2012;20(7):1426–36.
Smith SR, Weissman NJ, Anderson CM, Sanchez M, Chuang E, Stubbe S, et al. Behavioral modification and lorcaserin for overweight and obesity management (BLOOM) study group. Multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of lorcaserin for weight management. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(3):245–56.
Hollander P, Gupta AK, Plodkowski R, Greenway F, Bays H, Burns C, et al. Effects of naltrexone sustained-release/bupropion sustained-release combination therapy on body weight and glycemic parameters in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(12):4022–9.
Apovian CM, Aronne L, Rubino D, Still C, Wyatt H, Burns C, et al. A randomized, phase 3 trial of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR on weight and obesity-related risk factors (COR-II). Obesity. 2013;21(5):935–43.
Davidson MH, Hauptman J, DiGirolamo M, Foreyt JP, Halsted CH, Heber D, et al. Weight control and risk factor reduction in obese subjects treated for 2 years with orlistat: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999;281(3):235–42.
• Sahebkar A, Simental-Mendía LE, Reiner Ž, Kovanen PT, Simental-Mendía M, Bianconi V, Pirro M. Effect of orlistat on plasma lipids and body weight: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 33 randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol Res. 2017. Recent meta-analysis demonstrating optimization of lipid profiles with use of orlistat.
Derosa G, Maffioli P, Sahebkar A. Improvement of plasma adiponectin, leptin and C-reactive protein concentrations by orlistat: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;81(5):819–34.
Zelber–Sagi S, Kessler A, Brazowsky E, Webb M, Lurie Y, Santo M, et al. A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4(5):639–44.
Khan RA, Kapur P, Jain A, Farah F, Bhandari U. Effect of orlistat on periostin, adiponectin, inflammatory markers and ultrasound grades of fatty liver in obese NAFLD patients. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017;13:139–49.
Harrison SA, Fecht W, Brunt EM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Orlistat for overweight subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, prospective trial. Hepatology. 2009;49(1):80–6.
Torgerson JS, Hauptman J, Boldrin MN, Sjöström L. Xenical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects (XENDOS) study. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(1):155–61.
Shi YF, Pan CY, Hill J, Gao Y. Orlistat in the treatment of overweight or obese Chinese patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2005;22(12):1737–43.
Alberti KG, International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; Hational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; International Association for the Study of Obesity. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation. Circulation. 2009;120(16):1640–5.
Park YW, Zhu S, Palaniappan L, Heshka S, Carnethon MR, Heymsfield SB. The metabolic syndrome: prevalence and associated risk factor findings in the US population from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(4):427–36.
Mottillo S, Filion KB, Genest J, Joseph L, Pilote L, Poirier P, et al. The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(14):1113–32.
• Hall JE, do Carmo JM, da Silva AA, Wang Z, Hall ME. Obesity-induced hypertension: interaction of neurohumoral and renal mechanisms. Circ Res. 2015;116(6):991. Recent review on the mechanisms of obesity-related hypertension.
Katsurada K, Yada T. Neural effects of gut-and brain-derived glucagon-like peptide-1 and its receptor agonist. J Diabetes Investig. 2016;7(S1):64–9.
Saraiva FK, Sposito AC. Cardiovascular effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13(1):142.
Gadde KM, Allison DB, Ryan DH, Peterson CA, Troupin B, Schwiers ML, et al. Effects of low-dose, controlled-release, phentermine plus topiramate combination on weight and associated comorbidities in overweight and obese adults (CONQUER): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9774):1341–52.
Sharma AM, Golay A. Effect of orlistat-induced weight loss on blood pressure and heart rate in obese patients with hypertension. J Hypertens. 2002;20(9):1873–8.
Quehenberger O, Dennis EA. The human plasma lipidome. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(19):1812–23.
Bays HE, Toth PP, Kris-Etherton PM, Abate N, Aronne LJ, Brown WV, et al. Obesity, adiposity, and dyslipidemia: a consensus statement from the National Lipid Association. J Clin Lipidol. 2013;7(4):304–83.
• Grant RW, Dixit VD. Adipose tissue as an immunological organ. Obesity. 2015;23(3):512–8. Review article on the immune role of adipose tissue and systemic inflammation.
Jellinger PS, Handelsman Y, Rosenblit PD, Bloomgarden ZT, Fonseca VA, Garber AJ, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Guidelines for management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Endocr Pract. 2017;23(s2):1–87.
Belalcazar LM, Reboussin DM, Haffner SM, Hoogeveen RC, Kriska AM, Schwenke DC, et al. A 1-year lifestyle intervention for weight loss in individuals with type 2 diabetes reduces high C-reactive protein levels and identifies metabolic predictors of change. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(11):2297–303.
Canoy D, Boekholdt SM, Wareham N, Luben R, Welch A, Bingham S, et al. Body fat distribution and risk of coronary heart disease in men and women in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition in Norfolk cohort. Circulation. 2007;116(25):2933–43.
Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ôunpuu S, Bautista L, Franzosi MG, Commerford P, et al. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27000 participants from 52 countries: a case-control study. Lancet. 2005;366(9497):1640–9.
Tchkonia T, Thomou T, Zhu Y, Karagiannides I, Pothoulakis C, Jensen MD, et al. Mechanisms and metabolic implications of regional differences among fat depots. Cell Metab. 2013;17(5):644–56.
Pouliot MC, Després JP, Lemieux S, Moorjani S, Bouchard C, Tremblay A, et al. Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women. Am J Cardiol. 1994;73(7):460–8.
Santilli F, Simeone PG, Guagnano MT, Leo M, Maccarone MT, Di Castelnuovo A, et al. Effects of liraglutide on weight loss, fat distribution, and β-cell function in obese subjects with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(11):1556–64.
Charlton MR, Burns JM, Pedersen RA, Watt KD, Heimbach JK, Dierkhising RA. Frequency and outcomes of liver transplantation for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(4):1249–53.
Katsagoni CN, Georgoulis M, Papatheodoridis GV, Panagiotakos DB, Kontogianni MD. Effects of lifestyle interventions on clinical characteristics of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2017;68:119–32.
•• Armstrong MJ, Gaunt P, Aithal GP, Barton D, Hull D, Parker R, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. 2016;387(10019):679–90. Trial that demonstrated benefit of liraglutide in reversing NAFLD.
Carey DG, Jenkins AB, Campbell LV, Freund J, Chisholm DJ. Abdominal fat and insulin resistance in normal and overweight women: direct measurements reveal a strong relationship in subjects at both low and high risk of NIDDM. Diabetes. 1996;45(5):633–8.
Kaur J. A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract. 2014;11:2014.
Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;2002(346):393–403.
Gerstein HC. Do lifestyle changes reduce serious outcomes in diabetes? N Engl J Med. 2013;369(2):189.
James WP, Caterson ID, Coutinho W, Finer N, Van Gaal LF, Maggioni AP, et al. Effect of sibutramine on cardiovascular outcomes in overweight and obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(10):905–17.
Connolly HM, Crary JL, McGoon MD, Hensrud DD, Edwards BS, Edwards WD, et al. Valvular heart disease associated with fenfluramine–phentermine. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(9):581–8.
Nissen SE, Wolski KE, Prcela L, Wadden T, Buse JB, Bakris G, et al. Effect of naltrexone-bupropion on major adverse cardiovascular events in overweight and obese patients with cardiovascular risk factors: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315(10):990–1004.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Megin Myers, CRNP, for her critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
NA has consulted for Novo Nordisk. AA has consulted for Novo Nordisk and is a consultant for Andrew Technologies. ARC declares no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Nonstatin Drugs
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crawford, A.R., Alamuddin, N. & Amaro, A. Cardiometabolic Effects of Anti-obesity Pharmacotherapy. Curr Atheroscler Rep 20, 18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-018-0719-9
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-018-0719-9