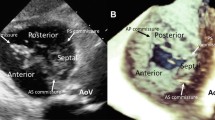
Abstract
Tricuspid valve (TV) disease commonly occurs in combination with left-sided heart disease. Despite the growing enthusiasm for developing novel minimally invasive therapies for the mitral or aortic valve, the TV disease formerly received less attention and was frequently left untreated. Strong evidence has increased the awareness of the impact of severe TV regurgitation on patient survival, functional capacity, and surgical risk. Preoperative TV accurate description is challenging because, unlike left-sided valves, a complete visualization of tricuspid annulus and all three leaflets in one view is routinely impossible by two-dimensional transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiography. Three-dimensional echocardiography (3DE) with its unrestricted imaging capabilities has sparked significant research interest for a better understanding and improved treatment of valvular heart disease. This review summarizes the current status of 3DE for the assessment of TV morphology and function, with its clinical applications and current limitations, as well as its potential implications for designing TV repair techniques.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Mascherbauer J, Maurer G. The forgotten valve: lessons to be learned in tricuspid regurgitation. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2841–3.
• Badano LP, Agricola E, Perez de Isla L, Gianfagna P, Zamorano JL. Evaluation of the tricuspid valve morphology and function by transthoracic real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2009;10:477–84. This review provides a practical guide to the assessment of the TV by transthoracic 3D and summarizes its main strengths over the conventional echocardiography for an accurate diagnosis of TV anatomy and function in various clinical settings.
Muraru D, Badano LP. Assessment of tricuspid valve morphology and function. In: Badano LP, Lang RM, Zamorano JL, editors. Textbook of real-time three dimensional echocardiography. London: Springler Verlag; 2011. p. 173–82.
Bruce CJ, Connolly HM. Right-sided valve diseases deserves a little more respect. Circulation. 2009;119:2726–34.
Fukuda S, Saracino G, Matsumara Y, et al. Three-dimensional geometry of the tricuspid annulus in healthy subjects and in patients with functional tricuspid regurgitation: a real-time, 3-dimensional echocardiographic study. Circulation. 2006;114:I-492–8.
Rawlins DB, Austin C, Simpson JM. Live three-dimensional paediatric intraoperative epicardial echocardiography as a guide to surgical repair of atrioventricular valves. Cardiol Young. 2006;16:34–9.
Seliem MA, Fedec A, Szwast A, et al. Atrioventricular valve morphology and dynamics in congenital heart disease as imaged with real-time 3-dimensional matrix-array echocardiography: comparison with 2-dimensional imaging and surgical findings. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007;20:869–76.
• Takahashi K, Mackie AS, Rebeyka IM et al. Two-dimensional versus transthoracic real-time three-dimensional echocardiography in the evaluation of the mechanisms and sites of atrioventricular valve regurgitation in a congenital heart disease population. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;23:726–34. The authors of this paper report the complementary role of transthoracic 3DE for the assessment of congenital abnormalities of the TV, using surgical findings as reference.
Attenhofer CH, Connolly HM, Dearani JA, Edwards WD, Danielson GK. Ebstein’s anomaly. Circulation. 2007;115:277–85.
Patel V, Nanda NC, Rajdev S, et al. Live/real time three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiographic assessment of Ebstein’s anomaly. Echocardiography. 2005;22:847–54.
Bharucha T, Anderson RH, Lim ZS, Vettukattil JJ. Multiplanar review of three-dimensional echocardiography gives new insights into the morphology of Ebstein’s malformation. Cardiol Young. 2010;20:49–53.
•• Bhattacharyya S, Toumpanakis C, Burke M, Taylor AM, Caplins ME, Davar J. Features of carcinoid heart disease identified by 2- and 3-dimensional echocardiography and cardiac MRI. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010;3:103–11. This paper details the characteristic features of the carcinoid heart disease, including the spectrum of TV involvement, in a large cohort of patient by various imaging modalities encompassing 2D and 3DE, magnetic resonance, and positron emission tomography.
Lin G, Nishimura RA, Connolly HM, Dearani JA, Sundt 3rd TM, Hayes DL. Severe symptomatic tricuspid valve regurgitation due to permanent pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:1672–5.
•• Seo Y, Ishizu T, Nakajima H, Sekiguchi Y, Watanabe S, Aonuma K. Clinical utility of 3-dimensional echocardiography in the evaluation of tricuspid regurgitation caused by pace-maker leads. Circ J 2008;72:1465–70. This study reports the superiority of 3DE over the 2D approach for accurately diagnosing pacemaker-induced tricuspid regurgitation by its ability to identify the spatial relationship between the lead and valve leaflets, particularly the posterior one.
Schnabel R, Khaw AV, von Bardeleben RS, et al. Assessment of the tricuspid valve morphology by transthoracic real-time-3D-echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2005;22:15–23.
Nishimura K, Okajama H, Inoue K, et al. Visualization of traumatic tricuspid insufficiency by three-dimensional echocardiography. Circ J. 2010;55:143–6.
Kamiya C, Ohara T, Nakatani S, et al. Traumatic tricuspid regurgitation caused by myocardial laceration: a three dimensional echocardiographic study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;903:903.e1–3.
Pearlman AS. Role of echocardiography in the diagnosis and evaluation of severity of mitral and tricuspid stenosis. Circulation. 1991;84(Suppl):I 193–7.
Faletra F, La Marchesina U, Bragato R, De Chiara F. hree dimensional transthoracic echocardiography images of tricuspid stenosis. Heart. 2005;91:499.
Naqvi TZ, Rafie R, Ghalichi M. Real-time 3D TEE for the diagnosis of right-sided endocarditis in patients with prosthetic devices. J Am Coll Cardiol Img. 2011;3:325–7.
Habib G, Badano L, Tribouilloy C, et al. Recommendations for the practice of echocardiography in infective endocarditis. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11:202–19.
Asch FP, Bieganski PM, Panza JA, Weissman NJ. Real-time 3-dimensional echocardiography evaluation of intracardiac masses. Echocardiography. 2006;23:218–24.
Dreyfus GD, Corbi PJ, Chan KM, Bahrami T. Secondary tricuspid regurgitation or dilatation: which should be the criteria for surgical repair? Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79:127–32.
Ton-Nu TT, Levine RA, Handschumacher MD, et al. Geometric determinants of functional tricuspid regurgitation:insights from 3-dimensional echocardiography. Circulation. 2006;114:143–9.
Matsunaga A, Duran CM. Progression of TR after repaired functional ischemic mitral regurgitation. Circulation. 2005;112(suppl):I-453–7.
Dreyfus GD, Corbi PJ, Chan KM, Bahrami T. Secondary tricuspid regurgitation or dilatation: which should be the criteria for surgical repair? Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79:127–32.
Colombo T, Russo C, Cilibert GR, et al. Tricuspid regurgitation secondary to mitral valve disease: tricuspid annulus function as guide to tricuspid valve repair. Cardiovasc Surg. 2001;9:369–77.
Anwar AM, Geleijnse MI, ten Cate FJ, Meijboom FJ. Assessment of tricuspid valve annulus size, shape and function using real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2006;5:683–7.
Sukmawan R, Watanabe N, Ogasawara Y, et al. Geometric changes of tricuspid valve tenting in tricuspid regurgitation secondary to pulmonary hypertension quantified by novel system with transthoracic real-time 3-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007;20:470–6.
•• Min SY, Song JM, Kim MK et al. Geometric changes after tricuspid annuloplasty and predictors of residual tricuspid regurgitation: a real-time three-dimensional echocardiography study. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2871–80. This nice study used 3DE to describe the geometric changes of tricuspid apparatus after annuloplasty. They reported that preoperative tenting volume, as a measure including both annulus size and leaflet tethering, and anteroposterior annulus diameter independently predict the surgical outcome.
Velayudhan DE, Brown TM, Nanda NC, et al. Quantification of tricuspid regurgitation by live three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiographic measurements of vena contracta area. Echocardiography. 2006;23:793–800.
Sugeng L, Shernan SK, Salgo IS, et al. Live 3-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography initial experience using the fully-sampled matrix array probe. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:446–9.
Sugeng L, Shernan SK, Weinert L, et al. Realtime three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography in valve disease: comparison with surgical findings and evaluation of prosthetic valves. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008;21:1347–54.
•• Vegas A, Meineri M. Three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography is a major advance for intraoperative clinical management of patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a core review. Anesth Analg. 2010;1548–73. This nice review presents the key features of the 3DE and its emerging clinical applications, including for the TV pathology, with a special focus on the utility of transesophageal examination in the operating room.
Anwar AM, Soliman OI, Nemes A, van Geuns RJ, Geleijnse MI, ten Cate FJ. Value of assessment of tricuspid annulus: real-time three-dimensional echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2007;23:701–5.
Disclosure
Conflicts of interest: D. Muraru: has received a research grant from GE Healthcare; L.P. Badano: has received research grants and is on the speakers bureau for GE Healthcare; C. Sarais: none; E. Soldà: none; S. Iliceto: none.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muraru, D., Badano, L.P., Sarais, C. et al. Evaluation of Tricuspid Valve Morphology and Function by Transthoracic Three-Dimensional Echocardiography. Curr Cardiol Rep 13, 242–249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-011-0176-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-011-0176-3