Abstract
Objective:
Liraglutide, a once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, induced clinically meaningful weight loss in a phase 2 study in obese individuals without diabetes. The present randomized phase 3 trial assessed the efficacy of liraglutide in maintaining weight loss achieved with a low-calorie diet (LCD).
Methods:
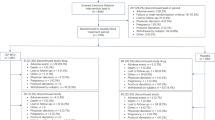
Obese/overweight participants (⩾18 years, body mass index ⩾30 kg m−2 or ⩾27 kg m−2 with comorbidities) who lost ⩾5% of initial weight during a LCD run-in were randomly assigned to liraglutide 3.0 mg per day or placebo (subcutaneous administration) for 56 weeks. Diet and exercise counseling were provided throughout the trial. Co-primary end points were percentage weight change from randomization, the proportion of participants that maintained the initial ⩾5% weight loss, and the proportion that lost ⩾5% of randomization weight (intention-to-treat analysis). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00781937.
Results:
Participants (n=422) lost a mean 6.0% (s.d. 0.9) of screening weight during run-in. From randomization to week 56, weight decreased an additional mean 6.2% (s.d. 7.3) with liraglutide and 0.2% (s.d. 7.0) with placebo (estimated difference −6.1% (95% class intervals −7.5 to −4.6), P<0.0001). More participants receiving liraglutide (81.4%) maintained the ⩾5% run-in weight loss, compared with those receiving placebo (48.9%) (estimated odds ratio 4.8 (3.0; 7.7), P<0.0001), and 50.5% versus 21.8% of participants lost ⩾5% of randomization weight (estimated odds ratio 3.9 (2.4; 6.1), P<0.0001). Liraglutide produced small but statistically significant improvements in several cardiometabolic risk factors compared with placebo. Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders were reported more frequently with liraglutide than placebo, but most events were transient, and mild or moderate in severity.
Conclusion:
Liraglutide, with diet and exercise, maintained weight loss achieved by caloric restriction and induced further weight loss over 56 weeks. Improvements in some cardiovascular disease-risk factors were also observed. Liraglutide, prescribed as 3.0 mg per day, holds promise for improving the maintenance of lost weight.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 November 2013
This article has been corrected since online publication and an erratum is also printed in this issue
References
World Health Organization. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 1998.
National Institutes of Health. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults--The Evidence Report. Obes Res 1998; 6 (Suppl 2): 51S–209S.
Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) Research Group. The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP): description of lifestyle intervention. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 2165–2171.
Wadden TA, Webb VL, Moran CH, Bailer BA . Lifestyle modification for obesity: new developments in diet, physical activity, and behavior therapy. Circulation 2012; 125: 1157–1170.
Wing RR, Jeffery RW, Hellerstedt WL . A prospective study of effects of weight cycling on cardiovascular risk factors. Arch Intern Med 1995; 155: 1416–1422.
Wing RR, Tate DF, Gorin AA, Raynor HA, Fava JL . A self-regulation program for maintenance of weight loss. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1563–1571.
Svetkey LP, Stevens VJ, Brantley PJ, Appel LJ, Hollis JF, Loria CM et al. Comparison of strategies for sustaining weight loss: the weight loss maintenance randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008; 299: 1139–1148.
Wadden TA, Neiberg RH, Wing RR, Clark JM, Delahanty LM, Hill JO et al. Four-year weight losses in the Look AHEAD study: factors associated with long-term success. Obesity 2011; 19: 1987–1998.
Garvey WT, Ryan DH, Look M, Gadde KM, Allison DB, Peterson CA et al. Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. Am J Clin Nutr 2012; 95: 297–308.
Sjostrom L, Rissanen A, Andersen T, Boldrin M, Golay A, Koppeschaar HPF et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. Lancet 1998; 352: 167–173.
Davidson MH, Hauptman J, Digirolamo M, Foreyt JP, Halsted CH, Heber D et al. Weight control and risk factor reduction in obese subjects treated for 2 years with orlistat: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999; 281: 235–242.
Apfelbaum M, Vague P, Ziegler O, Hanotin C, Thomas F, Leutenegger E . Long-term maintenance of weight loss after a very-low-calorie diet: a randomized blinded trial of the efficacy and tolerability of sibutramine. Am J Med 1999; 106: 179–184.
Smith SR, Weissman NJ, Anderson CM, Sanchez M, Chuang E, Stubbe S et al. Multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of lorcaserin for weight management. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 245–256.
Blonde L, Russell-Jones D . The safety and efficacy of liraglutide with or without oral antidiabetic drug therapy in type 2 diabetes: an overview of the LEAD 1-5 studies. Diabetes Obes Metab 2009; 11 (Suppl 3): 26–34.
Summary of product characteristics, Victoza 2012, http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/001026/WC500050017.pdf Accessed 14 Nov 2012.
Astrup A, Rossner S, Van Gaal L, Rissanen A, Niskanen L, Al Hakim M et al. Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lancet 2009; 374: 1606–1616.
Astrup A, Carraro R, Finer N, Harper A, Kunesova M, Lean ME et al. Safety, tolerability and sustained weight loss over 2 years with the once-daily human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide. Int J Obes 2012; 36: 843–854.
World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2000; 284: 3043–3045.
International Conference on Harmonisation. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. Good Clinical Practice. 1-May- 1996, http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Efficacy/E6_R1/Step4/E6_R1_Guideline.pdf Accessed 14 Nov 2012.
Mundt JC, Greist JH, Gelenberg AJ, Katzelnick DJ, Jefferson JW, Modell JG et al. Feasibility and validation of a computer-automated Columbia-Suicide severity rating scale using interactive voice response technology. J Psychiatr Res 2010; 44: 1224–1228.
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB . The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med 2001; 16: 606–613.
Corsetti JP, Cox C, Schulz TJ, Arvan DA . Combined serum amylase and lipase determinations for diagnosis of suspected acute pancreatitis. Clin Chem 1993; 39: 2495–2499.
Astrup A, Caterson I, Zelissen P, Guy-Grand B, Carruba M, Levy B et al. Topiramate: long-term maintenance of weight loss induced by a low-calorie diet in obese subjects. Obes Res 2004; 12: 1658–1669.
Food and Drug Administration. FDA Guidance for Industry: Developing products for weight management, 2007, http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/.../Guidances/ucm071612.pdf Accessed 14 Nov 2012.
Hill JO, Hauptman J, Anderson JW, Fujioka K, O'Neil PM, Smith DK et al. Orlistat, a lipase inhibitor, for weight maintenance after conventional dieting: A 1-y study. Am J Clin Nutr 1999; 69: 1108–1116.
Wadden TA, Berkowitz RI, Womble LG, Sarwer DB, Phelan S, Cato RK et al. Randomized trial of lifestyle modification and pharmacotherapy for obesity. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 2111–2120.
Wirth A, Krause J . Long-term weight loss with sibutramine: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001; 286: 1331–1339.
Munro JF, MacCusih AC, Wilson EM, Duncan LJ . Comparison of continuous and intermittent anorectic therapy in obesity. Br Med J 1968; 1: 352–354.
Wadden TA, Anderson DA, Foster GD . Two-year changes in lipids and lipoproteins associated with the maintenance of a 5 to 10% reduction in initial weight: some findings and some questions. Obes Res 1999; 7: 170–178.
Kelley DE, Wing R, Buonocore C, Sturis J, Polonsky K, Fitzsimmons M . Relative effects of calorie restriction and weight loss in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993; 77: 1287–1293.
Marso SP, Lindsey JB, Stolker JM, House JA, Martinez RG, Kennedy KF et al. Cardiovascular safety of liraglutide assessed in a patient-level pooled analysis of phase 2: 3 liraglutide clinical development studies. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2011; 8: 237–240.
NCEP report. Implications of recent clinical trials for the national cholesterol education program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines Endorsed by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, American College of Cardiology Foundation, and American Heart Association. Circulation 2004; 110: 227–239.
Grundy SM, Brewer HB Jr, Cleeman JI, Smith SC Jr, Lenfant C . Definition of Metabolic Syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association Conference on Scientific Issues Related to Definition. Circulation 2004; 109: 433–438.
The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. US Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. JAMA 2003; 289: 2560–2572.
Acknowledgements
We thank the study participants and acknowledge the members of the NN8022-1923 study group, their staff and clinical trial personnel, without whom this trial would not have been possible. We also thank Angela Harper, (Novo Nordisk A/S, Denmark), Edward S Kimball, (Novo Nordisk, Inc., USA), and Caroline Moran (University of Pennsylvania) for editorial and writing assistance. Liraglutide is a Novo Nordisk proprietary compound under development for chronic weight management. This work was funded by Novo Nordisk A/S, Denmark.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
PMH is an employee of Novo Nordisk, and also owns stock in the company. TAW serves on advisory boards for Novo Nordisk and Orexigen Pharmaceuticals. PH serves on an advisory board and is a consultant for Novo Nordisk. SK is a consultant for Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Vivus. KN is a consultant for Novo Nordisk and has done commercially sponsored research for Novo Nordisk. VW serves on advisory boards, has held paid lectures or has done commercially sponsored research for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim. LA is a consultant or receives research support from Amylin Pharmaceuticals, F Hoffman-La Roche, Abbott Laboratories, Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Orexigen Therapeutics, Vivus, GlaxoSmithKline Consumer Healthcare, LP, Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Zafgen. He has ownership interest in Cardiometabolic Support Network, LLC and Atlas Therapeutics.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Appendix
Appendix
NN8022-1923 Investigators
USA: Cory Anderson, Louis Aronne, Harold Bays, David C Bird, Thomas Blevins, Victor Elinoff, Kevin Furlong, William Gonte, Priscilla Hollander, Ronald Hsieh, Dean Karras, Robert Kaufmann, Samuel Klein, Thomas Littlejohn, Barry Lubin, Kevin Niswender, Robert Orr, John Pullman, Andrea Ramsay, Paul Rosenblit, Cynthia Strout, Mark Turner, Jeffrey Unger, Thomas Wadden, Bret Wittmer and Temala Zimmerman.
Canada: Vincent Woo, Joseph Berlingieri, Guy Tellier, Martyn Chilvers, Gordon Schacter, Andre Belanger, Pierre Martin, Jean Sebastien Gauthier and Sean Wharton.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wadden, T., Hollander, P., Klein, S. et al. Weight maintenance and additional weight loss with liraglutide after low-calorie-diet-induced weight loss: The SCALE Maintenance randomized study. Int J Obes 37, 1443–1451 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.120
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacotherapy for obesity: moving towards efficacy improvement
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2024)
-
Liraglutide 3.0 mg (Saxenda©) for Weight Loss and Remission of Pre-Diabetes. Real-World Clinical Evaluation of Effectiveness among Patients Awaiting Bariatric Surgery
Obesity Surgery (2024)
-
Obesity-induced and weight-loss-induced physiological factors affecting weight regain
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2023)
-
Current and future pharmacotherapies for obesity in children and adolescents
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2023)
-
Effect of liraglutide on cardiometabolic profile and on bioelectrical impedance analysis in patients with obesity and metabolic syndrome
Scientific Reports (2023)