Abstract
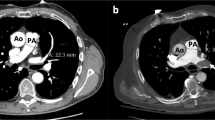
To retrospectively evaluate prognostic accuracy of subjective assessment of right ventricle (RV) enlargement on CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) images in comparison with objective measures of RV enlargement in patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). For 200 consecutive patients with acute PE, two readers blinded to patient outcomes subjectively determined whether the maximum RV diameter was greater than that of the left ventricle (LV) using axial CTPA images. For the objective measurements, RV/LV diameter ratios were calculated using axial images and 4-chamber reformatted images. For all assessments, sensitivities and specificities for predicting PE-related death within 30-days and a composite outcome including PE-related death or the need for intensive therapies were compared. The agreement between two readers was 91.5% (kappa = 0.83) and all other assessments had pair-wise agreement over 75% (kappa = 0.53–0.72). There was no significant difference in sensitivity between the subjective and objective methods for predicting both outcomes. The specificity for subjective RV enlargement (55.4–67.7%) was significantly higher than objective measures (45.8–53.1%), except for the 4-chamber views where, for one reader, the specificity of the subjective evaluation was higher but did not reach statistical significance. Complex measurements of RV/LV diameter ratios may not be needed to maximize the prognostic value from CTPA. The radiologist who interprets the CTPA images should report RV enlargement when the RV diameter subjectively appears larger than the LV.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carson JL, Kelley MA, Duff A, Weg JG, Fulkerson WJ, Palevsky HI, Schwartz JS, Thompson BT, Popovich J Jr, Hobbins TE et al (1992) The clinical course of pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 326(19):1240–1245
Stein PD, Fowler SE, Goodman LR, Gottschalk A, Hales CA, Hull RD, Leeper KV Jr, Popovich J Jr, Quinn DA, Sos TA, Sostman HD, Tapson VF, Wakefield TW, Weg JG, Woodard PK (2006) Multidetector computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 354(22):2317–2327. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa052367
Hunsaker AR, Lu MT, Goldhaber SZ, Rybicki FJ (2010) Imaging in acute pulmonary embolism with special clinical scenarios. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 3(4):491–500. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.109.855981
Reid JH, Murchison JT (1998) Acute right ventricular dilatation: a new helical CT sign of massive pulmonary embolism. Clin Radiol 53(9):694–698
Ghuysen A, Ghaye B, Willems V, Lambermont B, Gerard P, Dondelinger RF, D’Orio V (2005) Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography and prognostic significance in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Thorax 60(11):956–961. doi:10.1136/thx.2005.040873
Ghaye B, Ghuysen A, Willems V, Lambermont B, Gerard P, D’Orio V, Gevenois PA, Dondelinger RF (2006) Severe pulmonary embolism: pulmonary artery clot load scores and cardiovascular parameters as predictors of mortality. Radiology 239(3):884–891. doi:10.1148/radiol.2392050075
Collomb D, Paramelle PJ, Calaque O, Bosson JL, Vanzetto G, Barnoud D, Pison C, Coulomb M, Ferretti G (2003) Severity assessment of acute pulmonary embolism: evaluation using helical CT. Eur Radiol 13(7):1508–1514. doi:10.1007/s00330-002-1804-5
Schoepf UJ, Kucher N, Kipfmueller F, Quiroz R, Costello P, Goldhaber SZ (2004) Right ventricular enlargement on chest computed tomography: a predictor of early death in acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation 110(20):3276–3280. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000147612.59751.4C
Quiroz R, Kucher N, Schoepf UJ, Kipfmueller F, Solomon SD, Costello P, Goldhaber SZ (2004) Right ventricular enlargement on chest computed tomography: prognostic role in acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation 109(20):2401–2404. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000129302.90476.BC
Lu MT, Cai T, Ersoy H, Whitmore AG, Quiroz R, Goldhaber SZ, Rybicki FJ (2008) Interval increase in right-left ventricular diameter ratios at CT as a predictor of 30-day mortality after acute pulmonary embolism: initial experience. Radiology 246(1):281–287. doi:10.1148/radiol.2461062004
Araoz PA, Gotway MB, Trowbridge RL, Bailey RA, Auerbach AD, Reddy GP, Dawn SK, Webb WR, Higgins CB (2003) Helical CT pulmonary angiography predictors of in-hospital morbidity and mortality in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. J Thorac Imaging 18(4):207–216
van der Meer RW, Pattynama PM, van Strijen MJ, van den Berg-Huijsmans AA, Hartmann IJ, Putter H, de Roos A, Huisman MV (2005) Right ventricular dysfunction and pulmonary obstruction index at helical CT: prediction of clinical outcome during 3-month follow-up in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Radiology 235(3):798–803. doi:10.1148/radiol.2353040593
Stein PD, Matta F, Yaekoub AY, Goodman LR, Sostman HD, Weg JG, Hales CA, Hull RD, Leeper KV Jr, Beemath A, Saeed IM, Woodard PK (2009) Reconstructed 4-chamber views compared with axial imaging for assessment of right ventricular enlargement on CT pulmonary angiograms. J Thromb Thrombolysis 28(3):342–347. doi:10.1007/s11239-009-0331-5
Stein PD, Beemath A, Matta F, Goodman LR, Weg JG, Hales CA, Hull RD, Leeper KV Jr, Sostman HD, Woodard PK (2008) Enlarged right ventricle without shock in acute pulmonary embolism: prognosis. Am J Med 121(1):34–42. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.06.032
Bazeed MF, Saad A, Sultan A, Ghanem MA, Khalil DM (2010) Prediction of pulmonary embolism outcome and severity by computed tomography. Acta Radiol 51(3):271–276. doi:10.3109/02841850903524413
Dogan H, Kroft LJ, Huisman MV, van der Geest RJ, de Roos A (2007) Right ventricular function in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: analysis with electrocardiography-synchronized multi-detector row CT. Radiology 242(1):78–84. doi:10.1148/radiol.2421052089
Kamel EM, Schmidt S, Doenz F, Adler-Etechami G, Schnyder P, Qanadli SD (2008) Computed tomographic angiography in acute pulmonary embolism: do we need multiplanar reconstructions to evaluate the right ventricular dysfunction? J Comput Assist Tomogr 32(3):438–443. doi:10.1097/RCT.0b013e3180ca7818
Becattini C, Agnelli G, Vedovati MC, Pruszczyk P, Casazza F, Grifoni S, Salvi A, Bianchi M, Douma R, Konstantinides S, Lankeit M, Duranti M (2011) Multidetector computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism: diagnosis and risk stratification in a single test. Eur Heart J. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehr108
He H, Stein MW, Zalta B, Haramati LB (2006) Computed tomography evaluation of right heart dysfunction in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30(2):262–266
Lu MT, Ersoy H, Whitmore AG, Lipton MJ, Rybicki FJ (2007) Reformatted Four-Chamber and Short-Axis Views of the Heart Using Thin Section (</=2 mm) MDCT Images. Acad Radiol 14(9):1108–1112. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2007.05.019
Henzler T, Krissak R, Reichert M, Sueselbeck T, Schoenberg SO, Fink C (2010) Volumetric analysis of pulmonary CTA for the assessment of right ventricular dysfunction in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Acad Radiol 17(3):309–315. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2009.10.022
Golpe R, Perez-de-Llano LA, Castro-Anon O, Vazquez-Caruncho M, Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Veres-Racamonde A, Iglesias-Moreira C, Farinas MC (2010) Right ventricle dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension in hemodynamically stable pulmonary embolism. Respir Med. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2010.03.031
Contractor S, Maldjian PD, Sharma VK, Gor DM (2002) Role of helical CT in detecting right ventricular dysfunction secondary to acute pulmonary embolism. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26(4):587–591
Zhao DJ, Ma DQ, He W, Wang JJ, Xu Y, Guan CS (2010) Cardiovascular parameters to assess the severity of acute pulmonary embolism with computed tomography. Acta Radiol 51(4):413–419. doi:10.3109/02841851003649266
Nural MS, Elmali M, Findik S, Yapici O, Uzun O, Sunter AT, Erkan L (2009) Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography in the assessment of severity of acute pulmonary embolism and right ventricular dysfunction. Acta Radiol 50(6):629–637. doi:10.1080/02841850902902532
Lu MT, Cai T, Ersoy H, Whitmore AG, Levit NA, Goldhaber SZ, Rybicki FJ (2009) Comparison of ECG-gated versus non-gated CT ventricular measurements in thirty patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 25(1):101–107. doi:10.1007/s10554-008-9342-0
Araoz PA, Gotway MB, Harrington JR, Harmsen WS, Mandrekar JN (2007) Pulmonary embolism: prognostic CT findings. Radiology 242(3):889–897. doi:10.1148/radiol.2423051441
Habib G, Torbicki A (2010) The role of echocardiography in the diagnosis and management of patients with pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir Rev 19(118):288–299. doi:10.1183/09059180.00008110
Kang DK, Ramos-Duran L, Schoepf UJ, Armstrong AM, Abro JA, Ravenel JG, Thilo C (2010) Reproducibility of CT signs of right ventricular dysfunction in acute pulmonary embolism. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194(6):1500–1506. doi:10.2214/AJR.09.3717
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumamaru, K.K., Hunsaker, A.R., Bedayat, A. et al. Subjective assessment of right ventricle enlargement from computed tomography pulmonary angiography images. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 28, 965–973 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-011-9903-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-011-9903-5