ABSTRACT
Coronary artery calcium scoring is useful as a risk-stratification tool in coronary artery disease, and it outperforms other risk-assessment methods. American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines give the test a IIB recommendation in clinical scenarios in which risk stratification is uncertain. However, if the test is not used in the appropriate clinical setting, misinterpretation of the results can lead to unnecessary cardiac testing. This review provides the primary care provider with basic knowledge about the test’s clinical utility, interpretation, risks, and limitations.
Coronary artery calcium testing is useful in diagnosing subclinical coronary artery disease and in predicting the risk of future cardiovascular events and death.
Given the high negative predictive value of the test, it can also serve to reclassify risk in patients beyond traditional risk factors.
Along with shared decision-making, elevated calcium scores can guide the initiation of statin or aspirin therapy.
A high score in an asymptomatic patient should not trigger further testing without a comprehensive discussion of the risks and benefits.
The united states has seen a decline in fatal myocardial infarctions, largely thanks to early detection of coronary artery disease. Current guidelines on assessment of cardiovascular risk still rely on the traditional 10-year risk model in clinical practice. However, the predictive value of this approach is only moderate, and many coronary events occur in people considered to be at low or intermediate risk.
See related editorial, page 717
Coronary artery calcium scoring has emerged as a means of risk stratification by direct measurement of disease. Primary care providers are either using it or are seeing it used by consulting physicians, and its relatively low cost and ease of performance have contributed to its widespread use. However, downstream costs, radiation exposure, and lack of randomized controlled trials have raised concerns.
This article reviews the usefulness and pitfalls of coronary artery calcium scoring, providing a better understanding of the test, its limitations, and the interpretation of results.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS AND CALCIUM
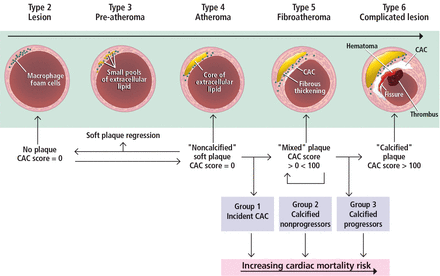
Atherosclerosis begins in the first few decades of life with a fatty streak in which lipoproteins are deposited in the intimal and medial layers of blood vessels (Figure 1). Inflammatory cells such as macrophages and foam cells are then recruited to the areas of deposition where they cause apoptosis, creating a necrotic core with calcium deposits.1–3
Pathogenic mechanism of atherosclerotic lesions and its relationship to the coronary artery calcium (CAC) score. A type 1 lesion (not depicted) contains lipoproteins that initiate an inflammatory response. A type 2 lesion contains an accumulation of foam cells. The type 3 lesion contains collections of extracellular lipid droplets. Eventually, these extracellular lipid pools form a lipid core, and a type 4 lesion is created. With time, this core develops a fibrous connective-tissue thickening that can calcify and give rise to a type 5 lesion detectable by imaging. Type 6 is a complicated lesion that can include thrombus from plaque rupture.
As the calcium deposits grow, they can be detected by imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT), and quantified to assess the extent of disease.4
CALCIFICATION AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
Coronary calcification occurs almost exclusively in atherosclerosis. Several autopsy studies5,6 and histopathologic studies7 have shown a direct relationship between the extent of calcification and atherosclerotic disease.
Sangiorgi et al7 performed a histologic analysis of 723 coronary artery segments. The amount of calcium correlated well with the area of plaque:
r = 0.89, P < .0001 in the left anterior descending artery
r = 0.7, P < .001 in the left circumflex artery
r = 0.89, P < .0001 in the right coronary artery.
Coronary artery calcium has also been associated with obstructive coronary artery disease in studies using intravascular ultrasonography and optical coherence tomography.8,9
TECHNICAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE TEST
First-generation CT scanners used for calcium scoring in the 1980s were electron-beam systems in which a stationary x-ray tube generated an oscillating electron beam, which was reflected around the patient table.10 A single, stationary detector ring captured the images.
These systems have been replaced by multidetector scanners, in which the x-ray tube and multiple rows of detectors are combined in a gantry that rotates at high speed around the patient.
Coronary calcium is measured by non-contrast CT of the heart. Thus, there is no risk of contrast-induced nephropathy or allergic reactions. Images are acquired while the patient holds his or her breath for 3 to 5 seconds. Electrocardiographic gating is used to reduce motion artifact.11,12 With modern scanners, the effective radiation dose associated with calcium testing is as low as 0.5 to 1.5 mSv,13,14 ie, about the same dose as that with mammography. The entire test takes 10 to 15 minutes.
Coronary calcium on CT is most commonly quantified using the Agatston score. Calcification is defined as a hyperattenuating lesion above the threshold of 130 Hounsfield units with an area of 3 or more pixels (1 mm2). The score is calculated based on the area of calcification per coronary cross-section, multiplied by a factor that depends on the maximum amount of calcium in a cross-section (a weighted value system based on Hounsfield units of dense calcification in each major coronary artery).15 The sum of calcium in the right coronary, left anterior descending, and left circumflex arteries gives the total Agatston calcium score.
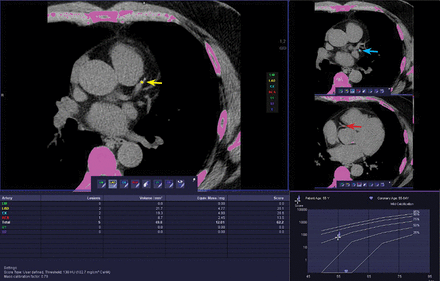
The results fall into 4 categories, which correlate with the severity of coronary artery disease, ranging from no significant disease to severe disease (Table 1). Other scores, which are not commonly used, include the calcium volume score16 and the calcium mass score.17 Figure 2 shows a screenshot from a coronary artery calcium scoring program.
Categories of coronary artery calcium scores
A screenshot from a standard calcium scoring program. The images show a small calcified plaque in the mid-left anterior descending artery (left upper panel, colored yellow), left circumflex artery (right upper panel, colored blue), and right coronary artery (right lower panel, colored red). The table in the left lower panel lists the results of the calcium score. (The Agatston score is listed as “Score”). The graph in the right lower panel shows the results of the individual patient relative to an age-and sex-matched patient population (eg, the MESA trial). This patient has a score of 62.2, indicating relatively mild calcification and falling on the 75% percentile for age, sex, and ethnicity in a control group.
CALCIUM SCORING AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL
Early multicenter studies evaluated the utility of calcium scoring to predict coronary stenosis in patients who underwent both cardiac CT and coronary angiography. The sensitivity of calcium scoring for angiographically significant disease was high (95%), but its specificity was low (about 44%).18
Budoff et al,19 reviewing these and subsequent results, concluded that the value of calcium scoring is its high negative predictive value (about 98%); a negative score (no calcification) is strongly associated with the absence of obstructive coronary disease.
Blaha et al20 concluded that a score of 0 would indicate that the patient had a low risk of cardiovascular disease. A test with these characteristics is helpful in excluding cardiovascular disease or at least in determining that it is less likely to be present in a patient deemed to be at intermediate risk.
CALCIUM SCORING AS A PROGNOSTIC TOOL
Early on, investigators recognized the value of calcium scoring in predicting the risk of future cardiovascular events and death.21–25
Predicting cardiovascular events
Pletcher et al21 performed a meta-analysis of studies that measured calcification in asymptomatic patients with subsequent follow-up. The summary-adjusted relative risk of cardiac events such as myocardial infarction, coronary artery revascularization, and coronary heart disease-related death rose with the calcium score:
2.1 (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.6–2.9) with a score of 1 to 100
4.2 (95% CI 2.5–7.2) with scores of 101 to 400
7.2 (95% CI 3.9-13.0) with scores greater than 400.
The meta-analysis was limited in that it included only 4 studies, which were observational.
Kavousi et al,22 in a subsequent meta-analysis of 6,739 women at low risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease based on the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) pooled cohort equation (10-year risk < 7.5%), found that 36.1% had calcium scores greater than 0. Compared with those whose score was 0, those with higher scores had a higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events. The incidence rates per 1,000 person-years were 1.41 vs 4.33 (relative risk 2.92, 95% CI 2.02–3.83; multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio 2.04, 95% CI 1.44–2.90). This study was limited because the population was mostly of European descent, making it less generalizable to non-European populations.
Calcium scoring has also been shown to be a strong predictor of incident cardiovascular events across different races beyond traditional risk factors such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and tobacco use.
Detrano et al,23 in a study of 6,722 patients with diverse ethnic backgrounds, found that the adjusted risk of a coronary event was increased by a factor of 7.73 for calcium scores between 101 and 300 and by a factor of 9.67 for scores above 300 (P < .001). A limitation of this study was that the patients and physicians were informed of the scores, which could have led to bias.
Carr et al24 found an association between calcium and coronary heart disease in a younger population (ages 32–46). In 12.5 years of follow-up, the hazard ratio for cardiovascular events increased exponentially with the calcium score:
2.6 (95% CI 1.0–5.7, P = .03) with calcium scores of 1 through 19
9.8 (95% CI 4.5–20.5, P < .001) with scores greater than 100.
Predicting mortality
Budoff et al,25 in an observational study of 25,253 patients, found coronary calcium to be an independent predictor of mortality in a multivariable model controlling for age, sex, ethnicity, and cardiac risk factors (model chi-square = 2,017, P < .0001). However, most of the patients were already known to have cardiac risk factors, making the study findings less generalizable to the general population.
Nasir et al26 found that mortality rates rose with the calcium score in a study with 44,052 participants. The annualized mortality rates per 1,000 person-years were:
0.87 (95% CI 0.72–1.06) with a score of 0
2.97 (95% CI 2.61–3.37) with scores of 1–100
6.90 (95% CI 6.02–7.90) with scores of 101–400
17.68 (95% CI 5.93–19.62) with scores higher than 400.
The mortality rate also rose with the number of traditional risk factors present, ie, current tobacco use, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and family history of coronary artery disease. Interestingly, those with no risk factors but a calcium score greater than 400 had a higher mortality rate than those with no coronary calcium but more than 3 risk factors (16.89 per 1,000 person-years vs 2.72 per 1,000 person years). As in the previous study, the patient population that was analyzed was at high risk and therefore the findings are not generalizable.
Shaw et al27 found that patients without symptoms but with elevated coronary calcium scores had higher all-cause mortality rates at 15 years than those with a score of 0. The difference remained significant after Cox regression was performed, adjusting for traditional risk factors.
Coronary artery calcium scoring vs other risk-stratification methods
Current guidelines on assessing risk still rely on the traditional 10-year risk model in clinical practice.25 Patients are thus classified as being at low, intermediate, or high risk based on their probability of developing a cardiovascular event or cardiovascular disease-related death in the subsequent 10 years.
However, the predictive value of this approach is only moderate,28 and a significant number of cardiovascular events, including sudden cardiac death, occur in people who were believed to be at low or intermediate risk according to traditional risk factor-based predictions. Because risk scores are strongly influenced by age,29 they are least reliable in young adults.30
Akosah et al31 reviewed the records of 222 young adults (women age 55 or younger, men age 65 or younger) who presented with their first myocardial infarction, and found that only 25% would have qualified for primary prevention pharmacologic treatments according to the National Cholesterol Education Program III guidelines.32,33 Similar findings have been reported regarding previous versions of the risk scores.33
Thus, risk predictions based exclusively on traditional risk factors are not sensitive for detecting young individuals at increased risk, and lead to late treatment of young adults with atherosclerosis, which may be a less effective strategy.34
The reliance on age in risk algorithms also results in low specificity in elderly adults. Using risk scores, elderly adults are systematically stratified in higher risk categories, expanding the indication for statin therapy to almost all men age 65 or older regardless of their actual vascular health, according to current clinical practice guidelines.35,36
Risk scores are based on self-reported history and single-day measurements, since this kind of information is readily available to the physician in the clinic. Moreover, our knowledge about genetic and epigenetic factors associated with the development of atherosclerosis is still in its infancy, with current guidelines not supporting genetic testing as part of cardiovascular risk assessment.37 Thus, a reliable measure of an individual’s lifelong exposure to a number of environmental and genetic factors that may affect cardiovascular health appears unfeasible.
Atherosclerosis is a process in which interactions between genetic, epigenetic, environmental, and traditional risk factors result in subclinical inflammation that could develop into clinically significant disease. Therefore, subclinical coronary atherosclerosis has been shown to be a strong predictor of future incident cardiovascular disease events and death. Thus, alternative approaches that directly measure disease, such as calcium scoring, may help further refine risk stratification of cardiovascular disease.
The MESA trial (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis), for instance, in 6,814 participants, found coronary calcium to provide better discrimination and risk reclassification than the ankle-brachial index, high sensitivity C-reactive protein level, and family history.38 Coronary calcium also had the highest incremental improvement of the area under the receiver operating curve when added to the Framingham Risk Score (0.623 vs 0.784).
Reclassifying cardiovascular risk also has implications regarding whether to start therapies such as statins and aspirin.
For considering statin therapy
Nasir et al39 showed that, in patients eligible for statin therapy by the pooled cohort equation, the absence of coronary artery calcium reclassified approximately one-half of candidates as not eligible for statin therapy. The number needed to treat to prevent an atherosclerotic cardiovascular event in the population who were recommended a statin was 64 with a calcium score of 0, and 24 with a calcium score greater than 100. In the population for whom a statin was considered, the number needed to treat was 223 with a calcium score of 0 and 46 for those with a score greater than 100. Moreover, 57% of intermediate-risk patients and 41% of high-risk patients based on the Framingham Risk Score were found to have a calcium score of 0, implying that these patients may actually be at a lower risk.
The Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography guidelines40 say that statin therapy can be considered in patients who have a calcium score greater than 0.
For considering aspirin therapy
Miedema et al41 studied the role of coronary artery calcium in guiding aspirin therapy in 4,229 participants in the MESA trial who were not taking aspirin at baseline. Those with a calcium score higher than 100 had a number needed to treat of 173 in the group with a Framingham Risk Score less than 10% and 92 with a Framingham Risk Score of 10% or higher. The estimated number needed to harm for a major bleeding event was 442. For those who had a score of 0, the estimated number needed to treat was 2,036 for a Framingham Risk Score less than 10% and 808 for a Framingham Risk Score of 10% or higher, with an estimated number needed to harm of 442 for a major bleeding event.
The Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography guidelines40 recommend considering aspirin therapy for patients with a coronary calcium score of more than 100.
McClelland et al42 developed a MESA risk score to predict 10-year risk of coronary heart disease using the traditional risk factors along with coronary calcium. The score was validated externally with 2 separate longitudinal studies. Thus, this may serve as another tool to help providers further risk-stratify patients.
COST-EFFECTIVENESS OF THE TEST
As coronary calcium measurement began to be widely used, concerns were raised about the lack of data on its cost-effectiveness.
Cost-effectiveness depends not only on patient selection but also on the cost of therapy. For example, if the cost of a generic statin is $85 per year, then calcium scoring would not be beneficial. However, if the cost of a statin is more than $200, then calcium scoring would be much more cost-effective, offering a way to avoid treating some patients who do not need to be treated.43
Hong et al43 showed that coronary calcium testing was cost-effective when the patient and physician share decision-making about initiating statin therapy. This is especially important if the patient has financial limitations, is concerned about side effects, or wants to avoid taking unnecessary medications.
RISKS AND DOWNSIDES OF CALCIUM SCORING
According to some reports, $8.5 billion is spent annually for low-value care.44 Many of the 80 million CT scans performed annually in the United States are believed to be unnecessary and may lead to additional testing to investigate incidental findings.45
Growing use of coronary calcium measurement has raised similar concerns about radiation exposure, healthcare costs, and increased downstream testing triggered by the detection of incidental noncardiac findings. For instance, Onuma et al46 reported that, in 503 patients undergoing CT to evaluate coronary artery disease, noncardiac findings were seen in 58.1% of them, but only 22.7% of the 503 had clinically significant findings.
Some of these concerns have been addressed. Modern scanners can acquire images in only a few seconds, entailing lower radiation doses than in the past.13,14 The cost of the test is currently less than $100 in many US metropolitan areas.47 However, further studies are needed to adequately and cost-effectively guide follow-up imaging of incidental noncardiac findings.48
An important limitation of calcium scoring for risk assessment is that no randomized controlled trial has evaluated the impact of preventive interventions guided by calcium scores on hard event outcomes. It can be argued that there have been plenty of observational studies that have shown the benefit of coronary calcium scoring when judiciously done in the appropriate population.49 Similarly, no randomized controlled trial has tested the pooled cohort equation and the application of statins based on its use with the current guidelines. The feasibility and cost of a large randomized controlled trial to assess outcomes after coronary artery calcium measurement must also be considered.
Another limitation of coronary calcium scoring is that it cannot rule out the presence of noncalcified atherosclerotic plaque, which often is more unstable and prone to rupture.
In addition, calcification in the coronary vascular bed (even if severe) does not necessarily mean there is clinically relevant coronary stenosis. For instance, an asymptomatic patient could have a coronary artery calcium score higher than 100 and then get a coronary angiogram that reveals only a 30% lesion in the left anterior descending coronary artery. This is because accumulation of (calcified) plaque in the vessel wall is accommodated by expansion of vessel diameter, maintaining luminal dimensions (positive remodeling). By definition, this patient does have coronary artery disease but would be best served by medical management. This could have been determined without an invasive test in an otherwise asymptomatic patient. Thus, performing coronary angiography based on a coronary artery calcium score alone would not have changed this patient’s management and may have exposed the patient to risks of procedural complications, in addition to extra healthcare costs. Therefore, the presence or absence of symptoms should guide the clinician on whether to pursue stress testing for invasive coronary angiography based on the appropriate use criteria.50,51
WHO SHOULD BE TESTED?
In the ACC/AHA 2013 guidelines,37 coronary calcium scoring has a class IIB recommendation in scenarios where it may appear that the risk-based treatment decision is uncertain after formal risk estimation has been done. As discussed above, a score higher than 100 could be a rationale for starting aspirin therapy, and a score higher than 0 for statin therapy. The current guidelines also mention that the coronary calcium score is comparable to other predictors such as the C-reactive protein level and the ankle-brachial index.
Compared with the ACC/AHA guidelines, the 2016 Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography guidelines and expert consensus recently have added more specifics in terms of using this test for asymptomatic patients at intermediate risk (10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease 5%–20%) and in selected patients with a family history of premature coronary artery disease and 10-year risk less than 5%.40,52 The 2010 ACC/AHA guidelines were more specific, offering a class IIA recommendation for patients who were at intermediate risk (Framingham Risk Score 10%–20%).53
The ACC/AHA cited cost and radiation exposure as reasons they did not give coronary calcium measurement a stronger recommendation.37 However, as data continue to come in, the guidelines may change, especially since low-dose radiation tools are being used for cancer screening (lungs and breast) and since the cost has declined over the past decade.
OUR APPROACH
Given the negative predictive value of the coronary calcium score, our approach has been to use this test in asymptomatic patients who are found to be at intermediate risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease based on the ACC/AHA risk calculation and are reluctant to start pharmacologic therapy, or who want a more personalized measure of coronary artery disease. This is preceded by a lengthy patient-physician discussion about the risks and benefits of the test.54
The patient’s risk can then be further clarified and possibly reclassified as either low or high if it doesn’t remain intermediate. A discussion can then take place on potentially starting pharmacologic therapy, intensive lifestyle modifications, or both.54,55 If an electronic medical record is available, CT results can be shown to the patient in the office to point out coronary calcifications. Seeing the lesions may serve an as additional motivating factor as patients embark on primary preventive efforts.56
Below, we describe cases of what we would consider appropriate and inappropriate use of coronary artery calcium scoring.
Example 1
A 55-year-old man presents for an annual physical and is found to have a 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease of 7%, placing him in the intermediate-risk category. Despite an extensive conversation about lifestyle modifications and pharmacologic therapy, he is reluctant to initiate these measures. He is otherwise asymptomatic. Would calcium scoring be reasonable?
Yes, it would be reasonable to perform coronary artery calcium scoring in an otherwise asymptomatic man to help reclassify his risk for a coronary vascular event. The objective data provided by the test could motivate the patient to undertake primary prevention efforts or, if his score is 0, to show that he may not need drug therapy.
Example 2
A 55-year-old man who has a family history of coronary artery disease, is an active smoker, and has diabetes mellitus presents to the clinic with 2 months of exertional chest pain that resolves with rest. Would coronary artery calcium scoring be reasonable?
This patient is symptomatic and is at high risk of coronary artery disease. Statin therapy is already indicated in the AHA/ACC guidelines, since he has diabetes. Therefore, calci um scoring would not be helpful, as it would not change this patient’s management. Instead, he would be best served by stress testing or coronary angiography based on the stability of his symptoms and cardiac biomarkers.
Example 3
A 30-year-old woman with no medical history presents with on-and-off chest pain at both exertion and rest. Her electrocardiogram is unremarkable, and cardiac enzyme tests are negative. Would coronary calcium scoring be reasonable?
This young patient’s story is not typical for coronary artery disease. Therefore, she has a low pretest probability of obstructive coronary artery disease. Moreover, calcium scoring may not be helpful because at her young age there has not been enough time for calcification to develop (median age is the fifth decade of life). Thus, she would be exposed to radiation unnecessarily at a young age.
What to do with an elevated calcium score?
Coronary artery calcification is now being incidentally detected as patients undergo CT for other reasons such as screening for lung cancer based on the US Preventive Services Task Force guidelines. Patients may also get the test done on their own and then present to a provider with an elevated score.
It is important to consider the entire clinical scenario in such patients and not just the score. If a patient presents with an elevated calcium score but has no symptoms and falls in the intermediate-risk group, there is evidence to suggest that he or she should be started on statin or aspirin therapy or both.
As mentioned above, an abnormal test result does not mean that the patient should undergo more-invasive testing such as cardiac catheterization or even stress testing, especially if he or she has no symptoms. However, if the patient is symptomatic, then further cardiac evaluation would be recommended.
SUMMARY
Measuring coronary artery calcium has been found to be valuable in detecting coronary artery disease and in predicting cardiovascular events and death. The test is relatively easy to perform, with newer technology allowing for less radiation and cost. It serves as a more personalized measure of disease and can help facilitate patient-physician discussions about starting pharmacologic therapy, especially if a patient is reluctant.
Currently, coronary calcium scoring has a class IIB recommendation in scenarios in which the risk-based treatment decision is uncertain after formal risk estimation has been done according to the ACC/AHA guideline. The Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography guideline and expert consensus documents are more specific in recommending the test in asymptomatic patients in the intermediate-risk group.
Limitations of calcium scoring include the possibility of unnecessary cardiovascular testing such as cardiac catheterization or stress testing being driven by the calcium score alone, as well as the impact of incidental findings. With increased reporting of the coronary calcium score in patients undergoing CT for lung cancer screening, the score should be interpreted in view of the entire clinical scenario.
- Copyright © 2018 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.