A 65-year-old man with numerous medical comorbidities presented with left-sided hemianopsia, hemineglect, weakness, and sensory loss lasting 1 day.
Results of computed tomography of the head were consistent with an acute ischemic stroke in the right-middle cerebral artery distribution. Perfusion imaging demonstrated minimal penumbra and a perfusion mismatch ratio of 1.0, a ratio suggesting that revascularization would not likely be beneficial.
In view of the duration of symptoms and the results of imaging, thrombolysis and acute neurointervention were deferred. Secondary stroke prevention was deemed the goal of care, and the stroke-care pathway was initiated.
The patient passed a bedside swallow examination with a mandibular removable partial denture in place, and was thus advanced to a level 2 mechanically altered dysphagia diet. The patient attempted to slowly self-feed for his first meal under close nursing supervision. After intake of a few bites of food, he complained of a cough and throat irritation, without symptoms of airway distress. Expeditious examination of his oral cavity revealed absence of his partial denture.
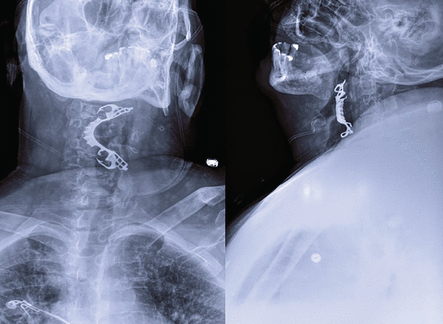
Soft-tissue radiography of the neck was urgently obtained (Figure 1) and revealed a metallic foreign body that looked like the patient’s partial denture in the pharynx at the level of the epiglottis, effacing the epiglottis.
Anteroposterior (left) and lateral (right) views on soft-tissue neck radiography show a metallic foreign body—the patient’s mandibular removable partial denture— within the pharynx at the level of the epiglottis, effacing the epiglottis.
The patient was immediately placed on nothing-by-mouth status and underwent emergency direct laryngoscopy to remove the foreign body.
His postoperative hospital course was complicated by septic shock secondary to aspiration pneumonia, requiring broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy, mechanical ventilation, and vasopressor support. The patient ultimately died of these complications during this hospital stay.
THE ROLE OF OROPHARYNGEAL SWALLOWING DEFICITS
In the United States, 800,000 people suffer a new or recurrent stroke each year, and stroke is the third leading cause of death after heart disease and cancer.
In patients with stroke, pneumonia is the medical complication causing the highest attributable proportion of deaths, accounting for nearly one-third of all deaths.1 Oropharyngeal swallowing dysfunction significantly increases the risk of this complication: patients with stroke who have dysphagia are 3 times more likely to develop respiratory infections than their counterparts without swallowing deficits, and those with aspiration are nearly 12 times more likely.2
While overt aspiration may be suspected in patients with a history of pneumonia, posterior territory lesions, impaired palatal and gag reflexes, coughing or choking during oral feeding, and voice changes after swallowing, these findings are not ubiquitous.3
Removable dentures pose a unique consideration, as they have been correlated with increased oral transit time and may be associated with an increased risk of aspiration, possibly due to impairment in oral cavity sensory function.4
In addition, although silent aspiration has been observed more frequently in patients with a history of orotracheal intubation and impaired velopharyngeal reflexes, the risk of silent aspiration is typically difficult to predict on the basis of the clinical history and neurologic evaluation. In patients with severe stroke and suspected oropharyngeal dysphagia, bedside swallowing assessments and pulse oximetry have a low diagnostic yield compared with videofluoroscopic evaluation.3,5
In this patient with severe stoke and a removable denture, a bedside clinical evaluation inaccurately led to the conclusion that it was safe to advance to a dysphagia diet, and he aspirated the denture and subsequently developed aspiration pneumonia and died.
DISCLOSURES
The authors report no relevant financial relationships which, in the context of their contributions, could be perceived as a potential conflict of interest.
- Copyright © 2021 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.