ABSTRACT
Familial hypercholesterolemia is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects the metabolism of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) through mutations in the gene for LDL receptor (LDLR), and less commonly in those for apolipoprotein B (APOB), proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 (PCSK9), and others. Patients with these mutations have elevated plasma levels of LDL-C and, as a result, an increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease beginning in childhood, leading to significant risk of illness and death.
Indices are available to help practitioners estimate a patient’s likelihood of having familial hypercholesterolemia based on lipid values, clinical presentation, and family history. Patients who likely have the disease should have further evaluation considered.
If a patient is found to have familial hypercholesterolemia, family members should be screened for it in a cascading process.
A statin is generally the first-line treatment, and a non-statin therapy such as ezetimibe can be added. PCSK9 inhibitors should also be considered if adequate LDL-C lowering is not achieved by statins or if the patient is statin-intolerant. Patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia may need LDL-C apheresis.
Familial hypercholesterolemia is the result of mutations in genes for proteins involved in the metabolism of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.1,2 Patients born with it can develop elevated LDL-C and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease at a young age,3 which can often be detected in childhood.
Strategies have been devised to detect the disease early for primary prevention, which is especially relevant now that novel lipid-lowering drugs are available.4–8 Often, the first opportunity for detection is during a routine checkup with the primary care physician.
Here, we provide an overview of familial hypercholesterolemia for general practitioners, including current diagnostic strategies, treatments, guidelines for management, and avenues for future research.
MUTATIONS IN LDLR AND OTHER GENES
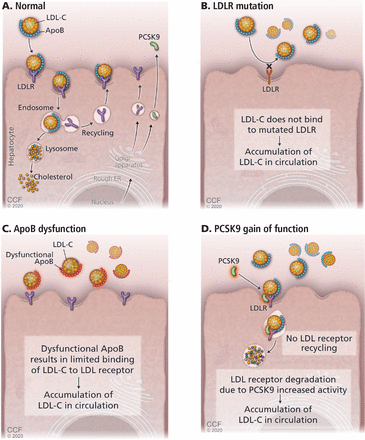
In more than 75% of cases of familial hypercholesterolemia, the LDL receptor is defective, owing to mutations in the LDLR gene.9 Less often, the problem is a mutation in a gene for another molecule that interacts with the LDL receptor, such as apolipoprotein B (APOB), proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 (PCSK9), or an unknown gene (Figure 1).2,9
(A) Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) binds to its receptor (LDLR), using apolipoprotein B (ApoB) as its ligand. Defects in LDLR (B) or ApoB (C) result in less binding of LDL-C, raising LDL-C levels. (D) Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9) binds to LDLR and escorts it into the interior of the hepatocyte, where it is destroyed, resulting in fewer receptors and higher LDL-C concentrations. Gain-of-function mutations in PCSK9 raise LDL-C levels.
Because familial hypercholesterolemia is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, most patients who have it are heterozygous, possessing 1 normal allele and 1 mutated allele.10 The prevalence of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia is about 1 in 220, based on large genetic studies.11 Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, in which the patient possesses 2 mutated alleles, is much less prevalent, with a frequency estimated at 1 in 300,000.10,12 Patients with homozygous disease face a worse prognosis.
The prevalence of familial hypercholesterolemia differs across ethnic groups, with higher frequencies of mutations in various parts of the world due to the founder effect. For instance, Finns, French-Canadians, Afrikaners, and Christian Lebanese populations have a higher prevalence of the disease.13 Racial differences have been shown as well; blacks have a slightly higher prevalence than whites or Hispanics.14
Although cardiovascular events tend to occur at an earlier age in men than in women, the prevalence of familial hypercholesterolemia is similar between sexes.4,14
ELEVATED RISK FROM AN EARLY AGE
Because people with familial hypercholesterolemia have elevated LDL-C levels from an early age, they also begin to have manifestations of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease early.3,15–17 Children with familial hypercholesterolemia have greater carotid intimal thickness than unaffected children by age 8.18 Coronary artery disease is evident in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia from age 17 in males and age 25 in females, and up to 25% of adolescents with familial hypercholesterolemia have coronary artery calcification.19,20
A study from Denmark showed an adjusted odds ratio for coronary artery disease of 3.3 in carriers of a familial hypercholesterolemia mutation.21 Similarly, the Spanish Familial Hypercholesterolemia Longitudinal Cohort Study (SAFEHEART) found the prevalence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease to be 3 times higher in people with familial hypercholesterolemia than in unaffected people.22
Clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is even more accelerated in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, in whom the first cardiovascular event usually occurs before age 30.23 Thus, early diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia is essential for risk stratification.
WHEN TO SUSPECT IT
Three sets of clinical criteria have been devised to identify patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.24–26 Each is based on a combination of:
Lipid levels, typically an LDL-C greater than 190 mg/dL
Family history of premature coronary artery disease or familial hypercholesterolemia
Clinical history
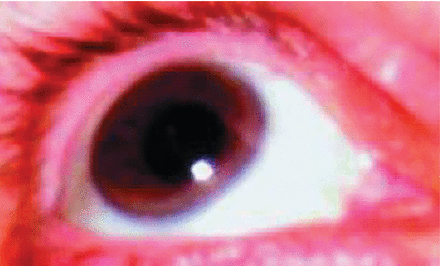
Physical signs such as xanthelasma (cholesterol deposits in the skin of the eyelids); xanthoma (deposits in connective tissue in and around extensor tendons—pathognomonic for this disease) (Figure 2)27 and arcus cornealis or corneal arcus (deposits along the corneal border) (Figure 3).27
Xanthomas of the Achilles tendons. Note the position used for examination, with the patient kneeling on a chair.
From Sibley and Stone, reference 27.
Corneal arcus.
From Sibley and Stone, reference 27.
The Dutch Lipid Network Criteria
The Dutch Lipid Network Criteria,24 the most widely used of the 3 sets of criteria, yields a score based on LDL-C level, physical findings, premature cardiovascular disease in relatives, and positive genetic testing if available (Table 1). A score higher than 8 makes the diagnosis “definite,” as 80% of people in that category were found to have a genetic mutation.28 One purpose of developing this set of criteria was to identify patients with familial hypercholesterolemia who did not have a family member with an established diagnosis.
The Dutch Lipid Clinic Network diagnostic criteria for familial hypercholesterolemia
The Simon Broome Registrar criteria
The Simon Broome Registrar criteria,25 developed in the United Kingdom, also rely on a combination of clinical, physical, and biochemical data (Table 2).13,16 Again, if certain clinical findings are met, a definite diagnosis can be made.
The Simon Broome diagnostic criteria for familial hypercholesterolemia
The MED-PED criteria
The Make Early Diagnosis and Prevent Early Deaths (MED-PED) criteria focus more on lipid levels and family history and less on clinical characteristics or genetic testing (Table 3).26 They were developed to be broadly applicable and were found to achieve 54% sensitivity and 98% specificity in detecting heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in the general population.26 The sensitivity improved to 88% when the criteria were used in patients with a first-degree relative with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, 85% in those with an affected second-degree relative, and 81% in those with an affected third-degree relative. Thus, the authors suggested performing biochemical testing of relatives of patients found to have heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia mutations, a process known as cascade screening.
MED-PED diagnostic criteria for probable heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
Which set of criteria is best?
The 3 sets of clinical screening criteria were compared in a retrospective study29 in 408 patients from 1995 through 2003. None outperformed the others, but when patients deemed to be in the “definite” diagnosis categories underwent genetic testing, the mutation detection rate was as low as 30% to 40%. The authors29 acknowledged that perhaps not all mutations were tested for, and polygenetic factors may have been overlooked. Regardless, they emphasized that the phenotype (ie, elevated LDL-C value, physical findings, and clinical history) confers enough of a cardiovascular risk to justify treatment, and that negative genetic testing should not stratify patients to lower risk categories.
This notion is endorsed by the International Atherosclerosis Society, which has proposed criteria for severe familial hypercholesterolemia based on LDL-C levels and evidence of subclinical or clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.30
What about homozygous disease?
The clinical criteria do not apply to patients who may have homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, which is much less common and more serious. However, the diagnosis can be suspected clinically if the patient has very high LDL-C levels (> 500 mg/dL if untreated, or > 300 mg/dL if on maximal lipid-lowering treatment) and has cholesterol deposits in the first decade of life, especially if both parents have heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.4
WHAT IS THE PATIENT’S RISK?
The Montreal FH Score31 predicts cardiovascular risk in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. It was devised by Paquette et al, based on a study in which they identified age, hypertension, low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, male sex, and smoking as independent risk factors (Table 4).31 A score higher than 20 points was associated with a cardiovascular risk 10 times greater than a score lower than 20 (odds ratio 10.3, 95% confidence interval 6.7–15.5, P < .001). The Montreal FH Score was validated in an independent cohort with familial hypercholesterolemia.32
The Montreal FH score to predict cardiovascular risk in familial hypercholesterolemia
GENETIC TESTING IS THE GOLD STANDARD
Genetic testing is the gold standard for diagnosing familial hypercholesterolemia. Most of the known mutations are in LDLR, but APOB, PCSK9, and potentially other genes involved in LDL-C catabolism can also have mutations. Several mutations remain unknown, and not finding a genetic mutation does not exclude the diagnosis, especially if there is strong phenotypic evidence.9
Finding a mutation also has prognostic value. At any LDL-C level, a gene-positive individual carries a higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease than does a gene-negative one.33 The type of LDLR mutation also carries its own risk.34 Thus, if you strongly suspect that a patient has the disease based on clinical diagnostic criteria, then genetic testing can be considered, with appropriate genetic counseling.35
Genetic testing may be particularly helpful in younger patients, especially if they have relatives with confirmed familial hypercholesterolemia. Though familial hypercholesterolemia can be diagnosed clinically based on lipid profile, patients with it have a higher burden of lifelong LDL-C exposure, which is likely a reason that gene-positive patients have a higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Genetics may also explain some degree of phenotypic heterogeneity, as more deleterious mutations (LDLR null) are associated with higher LDL-C levels and higher cardiovascular risk.30,36 Moreover, patients with severe heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia can have LDL-C concentrations that overlap with those of patients who have homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, and vice versa, leading to alternative therapeutic approaches.30 Polygenetic factors, gene-environment interactions, and gene-gene interactions can also allow for variations in familial hypercholesterolemia without extreme elevations in LDL-C, making genetic testing even more important for risk stratification.30
Rarely, genetic testing can also help in guiding therapy, as particular mutations (eg, null mutations of LDLR in homozygous patients) can make certain therapies ineffective.
CASCADE SCREENING OF RELATIVES
Identifying affected relatives is important so that they can be treated and potentially avoid atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Unfortunately, many remain unaware of their risk.37 Thus, screening strategies have been developed in the hope of rapid and cost-effective diagnosis.
This is primarily done through cascade screening, in which LDL-C measurement, genetic testing, or both are done in consenting relatives of patients (probands) identified with the disease. As more probands are identified, the process repeats itself by targeting more relatives. These strategies have been implemented in many European counties,38 and data from the SAFEHEART registry have indicated that identifying 9,000 cases of familial hypercholesterolemia in 10 years could prevent 847 coronary events and 203 coronary deaths, and could add 767 quality-adjusted life years.39
Cascade screening can be implemented in several ways, with outreach cascade screening in relatives of patients who have:
A worrisome lipid profile on a routine health screen but no symptoms
Early-onset atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and who meet clinical criteria for familial hypercholesterolemia
Persistently elevated lipid levels despite treatment, and a family history that raises the suspicion of familial hypercholesterolemia.
Genetic testing, when positive, allows very accurate cascade testing. However, genetic testing must follow established recommendations35 to maximize efficacy and minimize risk.40 Privacy and ethical issues are also raised, including questions about appropriate informed consent.40
In the United States, cascade screening can be challenging due to barriers in our healthcare system.41 Moreover, privacy policies mandate that the proband make first contact with family members, but the proband may have difficulty locating and getting in touch with them.41
Universal cholesterol screening of adults could help identify more people with familial hypercholesterolemia, but this strategy has not been fully implemented or recommended.42 Further, universal cholesterol screening is more common in adults than in children, whereas we need to diagnose the disease as early in life as possible.
Other strategies are being implemented to identify patients who may have familial hypercholesterolemia. For example, artificial intelligence systems that use machine learning techniques can explore electronic health records, billing codes, and laboratory data.43 Large-scale DNA sequencing may also help in finding cases that would not be detected.44 Though these novel techniques are intriguing, whether they would be cost-effective remains unclear.
TREATMENT SHOULD START EARLY
Starting lipid-lowering therapy early is as important as early detection of disease. In untreated heterozygous patients, the first coronary event occurs about 20 years earlier than in the general population.45 In untreated homozygous patients, the prognosis is even worse, with the first event often occurring in childhood.46
The type of mutation also affects treatment response. For instance, LDLR mutations can result in either a defective but somewhat functional LDL receptor or one with no functionality (null LDLR).35 Thus, cases of null LDLR mutations are more likely to be medically refractory, as lipid-lowering therapy often relies on somewhat functional LDL receptors.35
Lipid-lowering therapy in familial hypercholesterolemia can be with statins, non-statin drugs (eg, ezetimibe, PCSK9 inhibitors), and, rarely, LDL-C apheresis. Lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and exercise should accompany any medical therapy, even though they reduce LDL-C only modestly in adults with this disease.47
Statins are the first-line treatment
Reducing LDL-C levels is the primary goal, and high-dose statins are the first-line treatment. Statins inhibit the enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, resulting in decreased cholesterol production and increased LDL receptor expression on the surface of hepatocytes, which further reduces plasma LDL-C.9
Statin therapy should be started as soon as possible to help prevent cardiovascular events. In homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia patients, statin therapy is often started in the first decade of life.23 Of note, however, homozygous patients are more likely to have null LDLR mutations, which make statin therapy less effective.
Thanks to statin therapy, the prognosis for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia has improved in the last 30 years.48,49 In a randomized controlled trial in heterozygous patients, atorvastatin 80 mg lowered LDL-C levels by 50%.49 In another study,48 statin therapy reduced the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease from 60% at baseline to 10% (adjusted hazard ratio 0.18, 95% confidence interval 0.13–0.25). With statin therapy, the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in heterozygous patients was only slightly higher than in the general population (6.7 vs 4.1 events per 1,000 patient-years).48 Therefore, statin therapy has proven to be highly effective in terms of cost, morbidity, and mortality.4,48,49
Nonstatin therapies can be added
In cases in which statins do not effectively lower LDL-C, other lipid-lowering drugs can be considered as adjunctive therapy. The CASCADE, SAFEHEART, and other registries suggest that many patients with familial hypercholesterolemia cannot achieve their lipid goals with statins alone. Up to 50% require a second-line agent, and 20% require a PCSK9 inhibitor.50
Ezetimibe is a selective cholesterol absorption inhibitor that blocks uptake of cholesterol at both the enterocyte lumen and the hepatobiliary system.9 This leads to depletion of cholesterol stores and increased expression of LDL receptor, which further reduces plasma LDL-C.9 In patients already taking a statin, ezetimibe can further reduce LDL-C by 15% to 20% and is generally well tolerated in combination with statin therapy.1,51 National and international guidelines suggest ezetimibe as a second-line agent when LDL-C goals are not met with statins alone.50
Combination therapy with ezetimibe and simvastatin was shown to significantly reduce the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events after myocardial infarction.52 Though this study did not specifically target familial hypercholesterolemia patients, it further supports the benefit of lowering LDL-C in general in all high-risk populations.
Nonstatin therapies such as bile acid sequestrants, niacin, and fibrates are not well studied in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia.
Bile acid sequestrants form insoluble complexes of bile acid and cholesterol molecules that avoid capture by enterocytes.4,9 These complexes are then excreted. With less substrate for LDL-C, plasma levels can be decreased by 13% to 19%.4 Unfortunately, these medications are not well tolerated, which limits their use.
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3 or nicotinic acid, reduces free fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue, which impairs the liver’s ability to synthesize cholesterol and triglycer ide-containing particles.9 Unfortunately, the medication is not well tolerated and has not shown clinical efficacy in large randomized clinical trials in patients without familial hypercholesterolemia.53,54
Fibrates are typically used to lower triglyceride levels. Caution must be used when combining them with statins, as they can cause myopathies and other drug interactions.1
Newer agents have been developed that are currently reserved for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia patients, who commonly have null LDLR mutations.
Lomitapide is a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein inhibitor that prevents assembly of lipids onto proteins.9
Mipomersen is an antisense oligonucleotide that binds APOB mRNA and further decreases LDL-C generation in the liver.3
Both of these medications are poorly tolerated due to adverse effects, and thus they are reserved for patients at very high risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, such as those with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.9
PCSK9 inhibitors
Perhaps the most effective therapies in reducing LDL-C independently and in combination with statins are PCSK9 inhibitors.8 The US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency have approved 2 of these medications—evolocumab and alirocumab.
PCSK9 inhibitors are monoclonal antibodies that target circulating PCSK9, which normally degrades LDL receptor. More LDL receptor is therefore recycled to the hepatocyte surface and is available to remove more LDL-C from circulation.55
These medications are recommended when traditional lipid-lowering therapy cannot effectively lower LDL-C.55 They lower LDL-C levels by another 50% to 60% in addition to the reduction achieved by statins.56,57 They have also been shown to decrease LDL-C levels modestly (up to 20%) in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia who have almost no LDL receptor activity.58
Overall, these agents reduce major cardiovascular events in patients at high risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, like those with familial hypercholesterolemia.59,60 Further, they are generally well tolerated, but unfortunately, their cost can pose a barrier to both patients and providers.61 However, approvals from insurance companies are increasing, given the available evidence noted above.
LDL-C apheresis
LDL-C apheresis involves extracorporeal filtering of lipoproteins, using an indwelling venous catheter, either weekly or twice a week.44 It is usually reserved for patients at extremely high risk in whom medical therapies have been ineffective, or in those with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia who have a null LDLR mutation and no response to conventional lipid-lowering therapy.44 In fact, it is one of the only therapies shown to prolong survival in this group of patients.62
Factors to consider before referring patients for apheresis are cost, problems with venous access, and time. Despite its benefit in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, there is still a scarcity of evidence on its use, precluding standardized guidelines and limiting its use to a case-by-case basis.63
WHAT DO THE GUIDELINES SAY?
Several professional societies have published guidelines to help providers diagnose and manage familial hypercholesterolemia.6,35,64–66
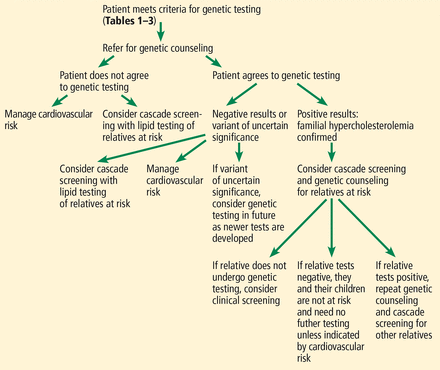
American professional societies generally agree on considering genetic testing for familial hypercholesterolemia in patients with elevated plasma LDL-C (usually > 190 mg/dL [> 4.9 mmol/L]), a family history of familial hypercholesterolemia, or who meet clinical criteria.35,65–67 The National Lipid Association64 and International Familial Hypercholesterolemia Foundation65 also recommend cascade screening when a mutation is identified (Figure 4).35
Algorithm for cascade screening.
Reprinted from Sturm AC, Knowles JW, Gidding SS, et al; Convened by the Familial Hypercholesterolemia Foundation. Clinical genetic testing for familial hypercholesterolemia: JACC Scientific Expert Panel. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018; 72(6):662–680. Copyright 2018, with permission from Elsevier.
For management, the American guidelines recommend lifestyle modifications in addition to lipid-lowering therapy.24,35,65,66 First-line drugs for patients with suspected familial hypercholesterolemia are high-intensity statins, which have class I recommendation (evidence or general agreement that the treatment is beneficial, useful, and effective) and a level of evidence of B-R (moderate, derived from 1 or more randomized controlled trials or meta-analyses of moderate-quality randomized controlled trials).50,65–67 The general consensus is that the initial LDL-C value should decrease by at least 50% in primary prevention settings. Alternative lipid-lowering therapies can be added if this goal is not reached, with the preferred second-line agent being ezetimibe, which has a class IIa recommendation (the weight of evidence or opinion is in favor of usefulness or efficacy), and a level of evidence of B-R.50
If patients strongly suspected of having familial hypercholesterolemia are on maximally tolerated statin therapy and ezetimibe and still have an LDL-C level of 100 mg/dL or higher or are statin-intolerant, then PCSK9 inhibitors can be considered (class IIb recommendation, level of evidence B-R).50 In secondary prevention cases, LDL-C goals should be 70 mg/dL or less, according to the 2018 American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association cholesterol guidelines, and 55 mg/dL or less according to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology (recommendation grade A, best level of evidence 1 [strong evidence]).66
These recommendations were primarily aimed at those with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. However, similar treatment algorithms exist for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Childhood diagnosis is essential, and there are lower thresholds for LDL-C apheresis.65,66 Referral to specialized centers for familial hypercholesterolemia should be strongly considered as soon as a diagnosis of heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia is established to aid in further screening, risk stratification, and treatment.
CALL FOR EARLIER DIAGNOSIS
Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic disease process that is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has designated familial hypercholesterolemia as a tier 1 genomic application, indicating that it imposes a significant public health burden.67 Thus, early diagnosis and treatment are essential to help reduce the burden of cardiovascular disease in these patients.
Unfortunately, a large percentage of people remain undiagnosed and at risk of cardiovascular events.68,69 Efforts are being made to identify patients earlier, through cascade screening, genome-wide DNA sequencing, or screening algorithms in large electronic health records.69 Earlier diagnosis should increase understanding of the disease and allow collaborations across specialties as we work to improve our care of familial hypercholesterolemia.
The Familial Hypercholesterolemia Foundation at www.thefhfoundation.org provides resources for patients and families.
Footnotes
Dr. Tang has disclosed serving as a consultant for MyoKardia and Sequana Medical.
- Copyright © 2020 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.