A 66-year-old man presented to the emergency department with 1 month of fevers, nonproductive cough, and progressively worsening dyspnea on exertion despite prior treatment for presumed community-acquired pneumonia.
He was a retired long-haul truck driver who had traveled throughout the United States. He said he had no domestic or occupational exposures to animals or unusual materials. He said he was sexually active with 1 female partner, using condoms. He had no risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, including intravenous drug use.
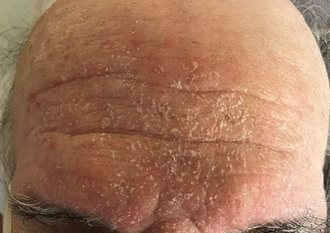
On further review of systems, he reported unintentional weight loss and an isolated facial rash that developed without a known trigger. Physical examination revealed mild tachypnea (22 breaths per minute), oxygen saturation of 89% on room air, clear lungs by chest auscultation, and a markedly erythematous, greasy, scaly rash on his forehead (Figure 1) and nasolabial folds.
The rash at presentation.
Possible causes of the rash included atopic dermatitis, tinea, malar rash of systemic lupus erythematosus, and rosacea. However, the location, quality, and appearance of the rash were most consistent with severe seborrheic dermatitis. The combination of seborrheic dermatitis, fevers, respiratory symptoms, hypoxia, and weight loss prompted an HIV test, which returned positive. When we reviewed the HIV test result with the patient, he revised his previous sexual history to include frequent, unprotected sexual intercourse with prostitutes at truck stops while he was a truck driver.
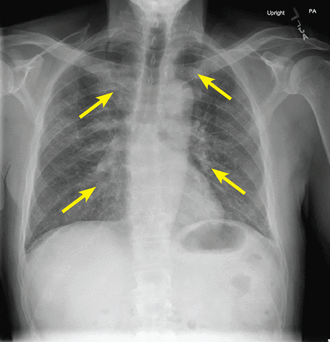
Chest radiography showed diffuse interstitial infiltrates (Figure 2). His CD4 count and percentage were low at 313 cells/mL and 27%, and a beta-D-glucan test for fungal infection was markedly elevated at greater than 500 pg/mL (positive ≥ 80 pg/mL), raising a strong suspicion for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, the most common HIV-associated opportunistic pulmonary infection.
Initial radiography showed diffuse interstitial infiltrates.
The patient was scheduled for bronchoalveolar lavage, but this procedure was canceled due to a shortage of staffing that prompted cancellation of nonemergency patient procedures.
In light of the patient’s history, physical examination, HIV test result, elevated beta-D-glucan, and negative workup including induced sputum for other fungal, viral, and bacterial etiologies, he was treated empirically for P jirovecii pneumonia1,2 with trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole for 21 days, and was started on combined bictegravir, emtricitabine, and tenofovir alafenamide for HIV.
His condition improved rapidly. On hospital day 5 his oxygen saturation was normal, and he was discharged home to complete his therapy.
SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS IN HIV INFECTION
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin disorder, observed worldwide in infancy and adulthood. HIV infection is a well-established risk factor, with an incidence between 30% and 80% compared with 1% to 3% in the general adult population.3,4 Seborrheic dermatitis is also associated with other intrinsic risk factors: immunocompromised state after organ transplant; neurologic and psychiatric disorders like Parkinson disease, epilepsy, and depression; and dermatologic disorders like acne, psoriasis, and rosacea.4
The severity ranges from mild and self-limiting in infants with “cradle cap,” to sometimes severe and persistent in adults with HIV infection and low CD4 counts (200–500 cells/mL).5
Treatment is multifaceted with consideration of the patient’s age, risk factors, chronicity of symptoms, and compliance with established therapies such as topical antifungals and corticosteroids.6
In summary, seborrheic dermatitis can serve as an invaluable bedside clue to HIV infection and can prompt earlier diagnosis in patients who report no risk factors for infection.
DISCLOSURES
The authors report no relevant financial relationships which, in the context of their contributions, could be perceived as a potential conflict of interest.
- Copyright © 2021 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.