ABSTRACT
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is mainly a clinical diagnosis based on typical symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation. Current guidelines indicate that patients with typical symptoms should first try a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). If reflux symptoms persist after 8 weeks on a PPI, endoscopy of the esophagus is recommended, with biopsies taken to rule out eosinophilic esophagitis. This review discusses the evidence for different medical, endoscopic, and surgical therapies and presents a management algorithm.
The diagnosis of GERD is mainly symptom-based and often does not require endoscopic confirmation.
Endoscopy is warranted in patients with red-flag symptoms such as dysphagia, anemia, weight loss, bleeding, and recurrent vomiting.
PPIs are the first-line medical therapy. Histamine 2 receptor antagonists are mainly used to treat breakthrough nocturnal symptoms.
Endoscopic and surgical options exist but are pursued only if medical therapy fails.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is common, accounting for more than 5.6 million physician visits each year.1 From 10% to 20% of adults in Western countries and nearly 5% of those in Asia experience GERD symptoms at least weekly.2 The prevalence of GERD symptoms is increasing by about 4% per year, in parallel with increases in obesity rates and reduction in prevalence of Helicobacter pylori over the past several decades.3 However, patients may not have symptoms of GERD even if they have objective evidence of it such as erosive esophagitis or Barrett esophagus.4
In 2015, the total direct economic impact of GERD and its complications was estimated to be over $18 billion, with use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) accounting for $12.4 billion, while the indirect costs driven by decreased work productivity were as much as $75 billion.1,5
TROUBLESOME SYMPTOMS, COMPLICATIONS
An international consensus group has defined GERD as a condition that develops when reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms with or without complications.6 Typical symptoms that lead to the diagnosis of GERD are regurgitation and heartburn. As much as 16% of the US population complains of regurgitation, and 6% report clinically troublesome heartburn.7 However, while these symptoms are specific for the disease, they are insensitive markers of reflux.
GERD symptoms can worsen with lying recumbent, especially after meals.
Of note, dysphagia can be a symptom of uncomplicated GERD, but its presence warrants more intensive examination and potential intervention, as it can be caused by strictures, rings, malignancy, or esophageal dysmotility.
Chest pain is another symptom often associated with GERD, but a cardiac cause should be considered and ruled out before GERD is considered.
Other symptoms of GERD include dyspepsia, nausea, bloating, sore throat, globus sensation, and epigastric pain.
A systematic review discovered that symptoms of GERD are less frequent in the elderly.8 However, on average, the severity of disease in the elderly was found to be greater than that in younger patients. Therefore, it was concluded that while the prevalence of documented GERD in older patients is less than that in younger patients, the actual rate of GERD is likely similar.
A subset of patients has extraesophageal symptoms of GERD such as asthma, laryngitis, pharyngitis, chronic cough, sinusitis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, dental erosions, and recurrent otitis media.6
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Since GERD was first described in 1879 by Heinrich Quincke, our understanding of its pathophysiology has slowly expanded and evolved.9 Factors now known to contribute to GERD include:
Transient lower esophageal sphincter (LES) relaxation
Sliding hiatal hernia
Low LES pressure
Acid pocket development due to poor mixing of acid with chyme in the proximal stomach
Increased gastroesophageal junction distensibility
Obesity
Delayed gastric emptying.9
Most symptoms are caused by acid reflux, but if symptoms persist on PPI therapy, they are likely due to either weakly acidic or weakly alkaline secretions.10,11
The distance up the esophagus that the reflux travels also plays a role in the symptoms of GERD. Acid reflux episodes that extend higher into the esophagus are associated with worse symptoms, regardless of the acidity of the bolus.12,13
Trimble et al13 found that patients with GERD have enhanced esophageal sensation and likely have heightened perceptions of normal nonacidic reflux events due to lower sensory thresholds. Another hypothesis is that sustained esophageal longitudinal muscle contractions may lead to transient ischemia of the esophageal wall, resulting in GERD symptoms in some patients.14
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
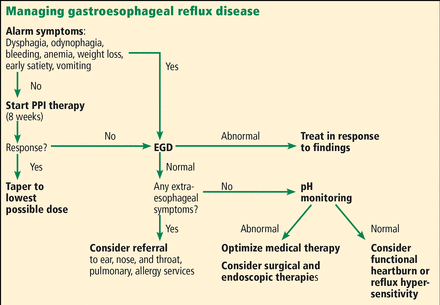
GERD is mainly a clinical diagnosis based on typical symptoms. Its diagnosis and management are summarized in Figure 1.
Approach to gastroesophageal reflux disease (PPI = proton pump inhibitor, EGD = esophagogastroduodenoscopy).
If no alarm symptoms, first try a PPI
Current guidelines indicate that patients with typical symptoms should first be given a trial of PPI treatment.15 However, patients with alarm symptoms including dysphagia, anemia, weight loss, bleeding, and recurrent vomiting should proceed directly to upper endoscopy.
There are limitations to this approach: a meta-analysis showed that a short course of PPI therapy has a 78% sensitivity and 54% specificity in accurately diagnosing GERD.16 In general, if typical symptoms resolve with an initial trial of a PPI, GERD should be diagnosed and the patient should continue taking a PPI daily.
Heartburn? Or heart attack?
In patients with chest pain, a cardiac condition should be ruled out before considering GERD. In one study,17 patients with noncardiac chest pain and endoscopic evidence of GERD had a significant response to PPI therapy, while those without endoscopic evidence had little or no response to therapy.17
Upper endoscopy
Endoscopy should be performed in any patient with the alarm symptoms described above, and also in patients whose symptoms do not respond to a PPI.
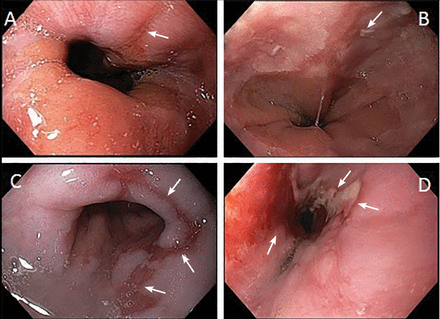
Abnormal endoscopic findings in GERD may include erosive esophagitis, strictures, and Barrett esophagus. However, many patients with GERD have normal findings on endoscopy. In 1999, the Los Angeles classification system was published and is now the standard method for classifying esophagitis (Figure 2).18,19 In addition, during endoscopy, biopsy samples from the esophagus should be obtained to rule out eosinophilic esophagitis.
Endoscopic views of esophagitis grades. (A) Grade A—1 or more mucosal breaks (arrow) no longer than 5 mm that do not extend between the tops of two mucosal folds. (B) Grade B—1 or more mucosal breaks (arrow) longer than 5 mm that do not extend between the tops of two mucosal folds. (C) Grade C—1 or more mucosal breaks (arrows) that are continuous between the tops of 2 or more mucosal folds, but involve less than 75% of the circumference. (D) Grade D—1 or more mucosal breaks (arrows) that involve at least 75% of the esophageal circumference.
Esophageal pH monitoring
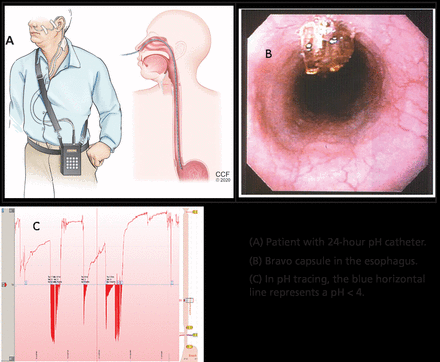
Esophageal pH monitoring is indicated in patients with persistent symptoms and normal findings on endoscopy before surgical or endoscopic interventions are considered. Esophageal pH monitoring can be done using a 24-hour transnasal pH or pH-impedance catheter or a 48-hour Bravo wireless capsule.
In clinical practice, pH testing is performed with the patient off PPI therapy when there is low clinical suspicion for GERD, whereas pH-impedance testing is performed while the patient is still on PPI therapy when there is higher likelihood of GERD, to evaluate refractory symptoms (Figure 3).20
(A) Patient with 24-hour pH catheter. (B) Bravo capsule in the esophagus. (C) In pH tracing, the blue horizontal line represents a pH < 4.
Barium esophagography is not indicated in the workup of reflux disease as it has poor sensitivity and specificity for GERD.
TREATMENT: LIFESTYLE, DRUG THERAPY, SURGERY
Lifestyle modifications
Lifestyle modifications are the first option for most patients.
Weight loss can help reduce and eliminate GERD symptoms. A prospective cohort study found that 81% of obese patients who completed a structured weight loss program had a reduction in symptoms, and 65% had complete resolution of symptoms.21 Another large retrospective study, with more than 15,000 patients, showed an association between improvement in GERD symptoms and reduction in body mass index (BMI) in obese patients who lost at least 2 kg/m2 in BMI (odds ratio 2.34).22
Diet, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation. Numerous studies have aimed to find foods that exacerbate reflux symptoms. Historically, patients have been advised to avoid smoking, chocolate, carbonated beverages, spicy food, fatty food, alcohol, and large meals. Thus far, no study has found improvement in GERD symptoms with cessation of either smoking or alcohol. In terms of food consumption, no food has been conclusively linked with increased GERD symptoms. No consistent associations have been established between GERD symptoms and fatty food, spicy food, coffee, carbonated beverages, chocolate, citrus, or mint.
Sleep position. Other studies have promoted elevating the head of the bed, sleeping in the left decubitus position, and, in those with nocturnal GERD symptoms, avoiding meals in the 2 to 3 hours before bedtime.23,24 A sleep positional therapy device has been shown to reduce acid exposure times and improve nocturnal reflux symptoms.25,26 This device places the user in the left decubitus position at an incline and has been an effective tool for those with nocturnal symptoms.
Drug therapy
If lifestyle interventions fail, drug treatment options are PPIs, histamine 2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs), and antacids.
PPIs are considered the therapy of choice for symptomatic relief and healing of erosive esophagitis. Compared with H2RAs, PPIs have been shown to provide improved healing rates and fewer relapses in patients with erosive esophagitis.27 To date, no study has shown a major difference in symptom control between the multiple PPIs. However, esomeprazole was shown, in a meta-analysis comparing it with other PPIs, to increase the probability of healing erosive esophagitis at 4 and 8 weeks.28
PPIs inhibit gastric acid secretion by inactivating the hydrogen potassium ATPase molecules of the parietal cell. Optimal acid suppression occurs when the proton pumps are activated as the parietal cell is maximally stimulated after a meal.
All PPIs should be taken 30 to 60 minutes before a meal for optimal pH control except dexlansoprazole, which employs dual delayed-release technology leading to sustained plasma drug concentrations; it can therefore be taken at any time of day. For patients with daytime symptoms, a PPI should be taken once daily in the morning, and for nighttime symptoms, the dose should be taken in the evening.
After the initial 8-week course of therapy, most patients with GERD should attempt to take the lowest dose required to manage their symptoms. For some, this could mean only taking the medication when symptoms arise. However, patients with severe erosive esophagitis (grade C or D), Barrett esophagus, and peptic strictures need long-term PPI treatment.
Adverse effects of PPIs. All patients need to be counseled about possible long-term adverse effects of PPIs.29 However, a recent randomized controlled trial found no association of PPIs with any adverse event when used for 3 years, with the possible exception of an increased risk of enteric infections.30
Vaezi et al29 reviewed the complications of PPI therapy and listed the relative risk and absolute excess risk in randomized controlled trials. From their data, we have calculated the number needed to harm, ie, the number of patients who would need to be treated for 1 year to observe 1 adverse effect:
Chronic kidney disease, 333–1,000
Dementia, 67–1,429
Bone fracture, 200–1,000
Campylobacter or Salmonella infection, 500–3,333
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (in patients with cirrhosis and ascites), 6–33
Clostridioides difficile infection, 1,111–no association
Micronutrient deficiencies, 250–333.
The authors found no association between long-term PPI use and the following:
Myocardial infarction
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
Pneumonia
Gastrointestinal malignancies.
Compared with earlier drugs, PPIs have been consistently shown to be superior at healing erosive esophagitis and relieving symptoms. PPIs can maintain intragastric pH higher than 4 for 15 to 21 hours daily, compared with the 8 hours that H2RAs can achieve.31 In a randomized trial, endoscopic remission of erosive esophagitis was found in 80.2% of those taking omeprazole 20 mg daily vs 39.4% in those taking ranitidine 150 mg daily.27
H2RAs appear useful in GERD for controlling nocturnal acid breakthrough. However, tachyphylaxis to these drugs develops rapidly, and they may therefore have a role only if used intermittently.32
Antacids, especially when combined with alginate preparations, are effective for reducing postprandial esophageal acid exposure.33
If first-line therapy fails
PPIs have immensely changed the landscape of treatment for GERD since their introduction, but up to 40% of patients with GERD find partial or no symptom relief with first-line therapies.34 In these nonresponders, it is important to determine compliance with PPIs, specifically the timing in relation to meals.
An 8-week course of therapy is needed to allow for healing, and patients should not be considered nonresponders until after this period unless alarm symptoms are present. For these patients, upper endoscopy should be performed within 2 weeks. For those without alarm symptoms but continued reflux in spite of therapy, endoscopy should be performed after 8 weeks, with biopsies of the esophagus to evaluate for eosinophilic esophagitis.
Esophageal impedance and pH testing are performed on these non- and partial responders while off PPIs to determine if there is persistent acidic or nonacidic reflux.
If results of pH and impedance testing are normal, the most common causes of continued symptoms are reflux hypersensitivity and functional heartburn. Reflux hypersensitivity is a heightened response to nonpathologic reflux, while functional heartburn is the presence of symptoms without any evidence of abnormal exposure. These patients should be reassured that their condition is benign, and they can be started on a pain modulator such as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, or tricyclic antidepressant.
If PPIs give partial relief, they should be continued, but they can be stopped for patients who have no response to them.
In patients found to have nonacid reflux, a trial of baclofen should be offered, as it has been shown to reduce the rate of lower esophageal sphincter transient relaxations.35
Alternative and investigational therapies
Alternative therapies are being investigated, but none have consistently shown significant benefits over placebo.
Therapies under investigation include reflux inhibitors, prokinetics, acupuncture, and hypnotherapy. Prokinetics, including metoclopramide and domperidone, have shown benefit in select patients with GERD but have been limited in their use due to associated central nervous system side effects and QT prolongation. New medical treatments for GERD on the horizon include potassium competitive acid blockers (vonaprazan) and bile acid sequestrant (IW3718) that binds to bile in the refluxate.
SURGICAL THERAPIES
Nissen fundoplication, first performed by Dr. Rudolph Nissen in 1955, gained popularity in the 1970s and is now the most widely performed antireflux surgery. It involves reducing the hiatal hernia and wrapping the gastric fundus partially or completely around the lower esophagus to restore the LES barrier.
Indications for the procedure are presence of a large hiatal hernia, reflux esophagitis or GERD symptoms refractory to medical therapy, or adverse effects of medical therapy.
A trial comparing laparoscopic fundoplication with esomeprazole therapy found similar remission rates after 3 years and a higher rate with esomeprazole after 5 years.36 While esomeprazole was associated with more symptoms of reflux compared with fundoplication, patients who underwent this surgery reported higher rates of dysphagia, flatulence, and bloating.
Antireflux surgery should be recommended with caution, as it can have severe side effects such as dysphagia, gas bloat syndrome, and flatulence and the intended effect may only be temporary, as up to 60% of patients will require antireflux medications regularly in the decade afterward.37 Esophageal manometry should be obtained before surgery to screen for esophageal aperistalsis, as this is an absolute contraindication to the procedure. Furthermore, manometry will exclude other motility disorders that can present similarly to GERD as discussed. Of note, antireflux surgery is not recommended in PPI nonresponders.15
The Linx procedure (magnetic sphincter augmentation; Torax Medical Inc., Shoreview, MN) is a minimally invasive alternative. It involves laparoscopic insertion of a band of magnetic beads around the LES, which allows passage of food and then closes to prevent acid reflux. The procedure is associated with improvement in symptom scores and reduced need for PPI therapy but not with consistent reduction in esophageal acid exposure.38
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is a surgical option for morbidly obese patients. A prospective study with 53 patients showed an improvement in GERD symptoms, reflux esophagitis, and esophageal acid exposure for more than 3 years following bypass.39
ENDOSCOPIC THERAPIES
Alternatively, several endoscopic treatments for GERD have been developed over the last 2 decades.40 These include:
Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) using the Esophyx device (EndoGastric Solutions, Redmond, WA)
Radiofrequency energy delivery to the LES (the Stretta procedure; Respiratory Technology Corporation, Houston, TX)
Endoscopic anterior fundoplication using the Medigus ultrasonic surgical endostapler (Medigus, Omer, Israel).
Of these, the first 2 have the most evidence.
TIF involves creation of a partial gastric wrap around the lower esophagus with an Esophyx device mounted on the endoscope. TIF is associated with symptom control and PPI reduction or cessation for at least 6 years and is a viable option for a select group of GERD patients with small hiatal hernias and preserved esophageal function.
A large randomized trial comparing TIF with PPIs showed symptomatic control in 67% vs 45% patients. TIF was associated with a reduction in esophageal acid exposure time from 9.3% to 6.4% and DeMeester score reduction from 33.6 to 23.9.41
In 2018, a meta-analysis was performed to compare TIF with Nissen fundoplication, a sham procedure, and PPIs.42 TIF was associated with a larger increase in quality of life measures, while Nissen fundoplication had a greater ability to improve physiologic parameters associated with GERD including LES pressure and the percentage of time the pH was less than 4.
The Stretta device was developed in 2000 and works by delivering thermal energy to the LES, which is postulated to increase sphincter thickness through scar tissue deposition, thereby reducing reflux. However in a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Stretta treatment did not reduce percentage of time when pH is less than 4 or increase LES pressure or ability to stop PPIs.43
- Copyright © 2020 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.